Google’s Universal Analytics Coming to an End in 2023
Google’s Universal Analytics (UA) will be coming to an end in 2023, marking a significant shift in the way businesses will track and analyze website and app data. This change signifies Google’s move to transition all users to Google Analytics 4 (GA4), a more advanced and comprehensive analytics platform designed to meet the needs of the modern digital landscape. Here’s what you need to know about this transition, its implications, and how to prepare for it.
Understanding the Transition from UA to GA4
Universal Analytics Overview:
- Universal Analytics, introduced in 2012, has been the standard for web analytics, providing insights into user behavior, traffic sources, and conversions.
- UA relies heavily on cookies and session-based data, which has become increasingly problematic with changes in privacy regulations and the decline of third-party cookies.
Google Analytics 4 Overview:
- GA4, launched in October 2020, represents a significant upgrade with a focus on privacy, cross-platform tracking, and machine learning.
- It uses an event-based data model, allowing for more flexible and detailed tracking of user interactions across websites and apps.
- GA4 is designed to work without cookies and includes features to comply with current and future privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Key Differences Between UA and GA4
- Data Model:
- UA: Session-based model, tracking user interactions within predefined sessions.
- GA4: Event-based model, providing more granular and flexible tracking of user interactions.
- Cross-Platform Tracking:
- UA: Primarily focuses on website tracking.
- GA4: Seamlessly integrates tracking for both websites and mobile apps, offering a holistic view of user journeys across platforms.
- Privacy and Data Control:
- UA: Relies on third-party cookies, which are being phased out.
- GA4: Designed to work without third-party cookies, incorporating privacy features like data anonymization and granular data retention controls.
- Machine Learning:
- UA: Limited machine learning capabilities.
- GA4: Enhanced machine learning features, providing predictive metrics such as purchase probability and churn probability.
- Reporting Interface:
- UA: Traditional reporting interface with predefined reports.
- GA4: More flexible and customizable reporting interface, allowing users to create tailored reports and explore data more intuitively.
Implications of the Transition
- End of Data Processing in UA:
- Starting from July 1, 2023, UA will stop processing new data, and users will need to transition to GA4 to continue tracking their website and app data.
- Historical Data Access:
- Users will have access to their previously processed data in UA for at least six months after the end date. Google recommends exporting important reports and data during this period.
- Learning Curve:
- GA4 introduces new concepts and reporting interfaces, which may require users to invest time in learning and adapting to the new platform.
- Enhanced Capabilities:
- Despite the learning curve, GA4 offers advanced features that can provide deeper insights and more robust tracking capabilities, benefiting businesses in the long run.
Preparing for the Transition
- Set Up GA4 Property:
- Create a GA4 property alongside your existing UA property to start collecting data in parallel. This will allow you to familiarize yourself with GA4 while maintaining your existing analytics setup.
- Understand GA4 Features:
- Explore the new features and capabilities of GA4, such as event tracking, enhanced measurement, and predictive metrics. Google Analytics Academy offers courses to help you get up to speed.
- Migrate Key Tracking:
- Identify critical metrics and tracking setups in UA and replicate them in GA4. This includes setting up events, goals (now conversions), and custom dimensions/metrics.
- Export Historical Data:
- Before UA stops processing data, export important historical reports and data from UA for future reference.
- Update Stakeholders:
- Communicate the transition plan and timeline to stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aware of the changes and how they might impact reporting and analysis workflows.
- Leverage GA4 Integrations:
- Take advantage of GA4’s integrations with other Google tools, such as Google Ads and BigQuery, to enhance your data analysis capabilities.
Why we care
The transition from Google’s Universal Analytics (UA) to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is significant for several reasons, and it’s important to understand why businesses, marketers, and web analysts should care about this change. Here are the key reasons why this transition matters:
1. Enhanced Data Privacy and Compliance
Evolving Privacy Regulations:
- Privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have changed how data can be collected and used. GA4 is designed to comply with these regulations by offering more robust data privacy features.
Cookie-Less Tracking:
- With the decline of third-party cookies, GA4’s event-based model allows for more accurate data collection without relying on cookies. This ensures that tracking remains effective even as browsers implement stricter privacy controls.
2. Advanced Insights and Predictive Analytics
Machine Learning Integration:
- GA4 leverages machine learning to provide predictive insights such as purchase probability and churn probability. These insights can help businesses make data-driven decisions and optimize their marketing strategies.
Enhanced Reporting:
- The new analytics platform offers more customizable and flexible reporting tools, allowing users to tailor reports to their specific needs and gain deeper insights into user behavior.
3. Improved Cross-Platform Tracking
Unified User Journey:
- GA4 allows for seamless tracking across websites and mobile apps. This unified approach helps businesses understand the complete user journey, from initial interaction to conversion, across multiple devices and platforms.
Comprehensive Data Collection:
- By integrating web and app data, GA4 provides a more holistic view of user interactions, helping businesses create more effective marketing strategies and improve user experiences.
4. Future-Proofing Your Analytics
Adaptation to Technological Changes:
- As digital landscapes evolve, GA4 is built to adapt to future changes in technology and user behavior. Adopting GA4 ensures that businesses are prepared for ongoing advancements and shifts in digital analytics.
Long-Term Support:
- With Universal Analytics ending in 2023, transitioning to GA4 ensures that businesses continue to receive support and updates from Google, maintaining the integrity and functionality of their analytics setup.
5. Enhanced User Engagement and Experience
Event-Driven Data Model:
- GA4’s event-based model provides more detailed and granular data about user interactions. This helps businesses understand how users engage with their site or app, allowing for targeted improvements and better user experiences.
Automatic Tracking:
- GA4 includes enhanced measurement features that automatically track certain user interactions, such as scrolls, outbound clicks, and video engagements, without requiring additional configuration.
6. Greater Control and Customization
Flexible Data Collection:
- GA4 allows for more flexible event tracking and customization. Businesses can define and track the events that matter most to them, providing more relevant insights.
Advanced Segmentation:
- The new platform offers advanced segmentation capabilities, enabling businesses to create custom audiences and segments based on specific criteria, which can be used for more precise targeting and analysis.
7. Integration with Google Ecosystem
Google Ads and BigQuery:
- GA4’s integration with Google Ads provides better attribution and conversion tracking, helping businesses optimize their ad spend and improve ROI. The integration with BigQuery allows for advanced data analysis and reporting capabilities.
Enhanced Attribution Models:
- GA4 includes more sophisticated attribution models that help businesses understand the contribution of different marketing channels to conversions, leading to more informed marketing strategies.
8. Actionable Data for Better Decision-Making
Real-Time Reporting:
- GA4’s real-time reporting capabilities enable businesses to monitor user activity as it happens, allowing for quicker responses to emerging trends and issues.
Custom Dashboards and Reports:
- Businesses can create custom dashboards and reports tailored to their specific needs, ensuring that the most important data is readily accessible for decision-making.
9. Increased Competitive Advantage
Staying Ahead:
- Early adoption of GA4 allows businesses to stay ahead of the curve, leveraging the latest tools and features to gain a competitive edge in their industry.
Optimized Marketing Efforts:
- By utilizing GA4’s advanced features, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts, improve customer engagement, and drive higher conversions and revenue.
How to get started in Google Analytics 4
Getting started with Google Analytics involves setting up an account, integrating it with your website, and understanding its basic functionalities. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you begin your journey with Google Analytics:
Step 1: Create a Google Analytics Account
- Sign Up:
- Go to Google Analytics.
- Click on the “Start for free” button.
- Google Account:
- Sign in with your Google account. If you don’t have one, create a Google account first.
- Account Setup:
- Click on “Start Measuring.”
- Enter an account name. This can be your business name or any identifier you prefer.
- Configure the data sharing settings according to your preferences and click “Next.”
Step 2: Set Up a Property
- Property Details:
- Enter a property name. This is usually the name of your website.
- Select your reporting time zone and currency.
- Click “Next.”
- Business Information:
- Select your business size and industry category.
- Choose how you intend to use Google Analytics (e.g., measure customer engagement, optimize ad spend).
- Click “Create.”
- Accept Terms:
- Review the Google Analytics Terms of Service and the Data Processing Amendment.
- Accept the terms to proceed.
Step 3: Set Up a Data Stream
- Choose Platform:
- Select the platform you want to measure (Web, Android app, or iOS app). For most users, this will be “Web.”
- Set Up Data Stream:
- Enter your website URL and stream name.
- Click on “Create stream.”
Step 4: Add the Google Analytics Tracking Code to Your Website
- Get the Tracking Code:
- After setting up the data stream, you’ll be provided with a Global Site Tag (gtag.js) code.
- Install the Code:
- Copy the tracking code.
- Paste the tracking code into the
<head>section of your website’s HTML code on every page you want to track.
Step 5: Verify Tracking Code Installation
- Check in Google Analytics:
- Go to the “Admin” section in Google Analytics.
- Under the property, go to “Data Streams.”
- Select your data stream and check if it’s receiving data.
- Use Google Tag Assistant:
- Install the Google Tag Assistant Chrome extension to verify the tracking code is working correctly.
Step 6: Explore Google Analytics Dashboard
- Overview:
- The Home section provides an overview of your site’s key metrics, such as active users, traffic sources, and more.
- Reports:
- Real-Time: See who is on your site in real-time.
- Audience: Understand who your visitors are, including demographics, interests, and behavior.
- Acquisition: Learn how visitors find your website.
- Behavior: Analyze how visitors interact with your site.
- Conversions: Track goals and e-commerce transactions.
Step 7: Set Up Goals
- Define Goals:
- Go to the “Admin” section.
- Under the property, select “Goals.”
- Click “New Goal” and set up goals based on actions you want to track, such as form submissions, purchases, or time spent on the site.
- Goal Types:
- Destination: Track when a user reaches a specific page.
- Duration: Measure the time users spend on your site.
- Pages/Screens per session: Monitor the number of pages viewed in a session.
- Events: Track specific interactions like clicks or video views.
Step 8: Link Google Analytics with Other Tools
- Google Ads:
- If you run Google Ads campaigns, link your Google Ads account with Google Analytics to track ad performance.
- Go to “Admin” > “Google Ads Linking” and follow the instructions.
- Search Console:
- Link Google Search Console to get insights into organic search performance.
- Go to “Admin” > “Property Settings” > “Adjust Search Console” and add your site.
Step 9: Customize Your Dashboard
- Create Custom Dashboards:
- Use the “Customization” section to create dashboards tailored to your needs.
- Add widgets to track key metrics, such as traffic sources, conversion rates, and user behavior.
- Saved Reports:
- Save custom reports for easy access to the metrics you frequently monitor.
Step 10: Learn and Improve
- Google Analytics Academy:
- Take advantage of free courses available on the Google Analytics Academy to deepen your understanding.
- Regular Review:
- Regularly review your Google Analytics data to identify trends, track performance, and make data-driven decisions to improve your website and marketing efforts.
Realtime refresh in GA 4
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) provides powerful real-time data capabilities that allow you to monitor user activity as it happens on your website or app. Real-time data can help you understand immediate trends, track the effectiveness of recent campaigns, and quickly identify and resolve issues. Here’s a detailed guide on how to use real-time data in GA4:
Accessing Real-Time Reports in GA4
- Login to Google Analytics:
- Go to Google Analytics and log in with your credentials.
- Select the GA4 Property:
- Choose the GA4 property for which you want to view real-time data.
- Navigate to Real-Time Reports:
- In the left-hand menu, click on “Reports.”
- Under the “Reports” section, find and click on “Real-Time.”
Understanding Real-Time Reports in GA4
The real-time reports in GA4 provide various insights into the current activity on your site or app. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and what you can learn from each:
- Overview:
- Users: See the number of users currently active on your site.
- Top Locations: View where your current users are located geographically.
- Top Events: Monitor the events that are currently being triggered the most.
- Top Pages: See which pages are being viewed the most in real-time.
- User Snapshots:
- User Properties: Get detailed information about individual users, such as their location, device, and active session.
- Event Stream: Track the sequence of events a particular user triggers during their session.
- Traffic Sources:
- Understand where your real-time traffic is coming from, including direct traffic, organic search, social media, and more.
- Content:
- Page Views: See the current top pages being viewed by users.
- Screens: For apps, view the top screens being accessed.
- Conversions:
- Monitor real-time conversions to see how well your goals are being met.
- Identify which events are leading to conversions in real-time.
Using Real-Time Data for Insights and Actions
- Monitor Campaign Performance:
- Use real-time data to track the immediate impact of your marketing campaigns. For instance, if you’ve just launched an email campaign, you can see how many users are visiting your site from the email links.
- Identify and Resolve Issues:
- Real-time data can help you quickly spot any issues, such as broken links, slow-loading pages, or other technical problems. If you notice a sudden drop in user activity, it could indicate a problem that needs immediate attention.
- Understand User Behavior:
- By analyzing the sequence of events users trigger, you can gain insights into their behavior and preferences. This can help you optimize your site or app to better meet their needs.
- Geographical Insights:
- Real-time location data can be useful for local promotions or understanding regional engagement. If you’re running a promotion in a specific area, you can see how well it’s performing in real-time.
- Content Engagement:
- Identify which content is currently attracting the most attention. This can help you understand what’s resonating with your audience and guide future content creation efforts.
Setting Up Real-Time Alerts
GA4 allows you to set up custom alerts to notify you when certain conditions are met in real-time. Here’s how to set them up:
- Go to Admin:
- In the left-hand menu, click on “Admin.”
- Create a Custom Alert:
- Under the “Property” column, click on “Custom Definitions” and then “Custom Alerts.”
- Click on “New Alert.”
- Configure the Alert:
- Name your alert and define the conditions that will trigger it. For example, you can set an alert for a sudden spike in traffic, a specific event being triggered frequently, or a drop in active users.
- Choose how you want to be notified (e.g., email or mobile notification).
- Save the Alert:
- Click “Save” to activate your custom alert.
Best Practices for Using Real-Time Data in GA4
- Frequent Monitoring:
- Regularly check real-time reports to stay updated on user activity and quickly respond to changes.
- Combine with Historical Data:
- Use real-time data in conjunction with historical data to understand trends and make informed decisions. Real-time data provides immediate insights, while historical data offers context and patterns over time.
- Customize Reports:
- Customize your real-time reports to focus on the metrics and dimensions that matter most to your business. This can include specific events, user segments, or traffic sources.
- Test and Optimize:
- Use real-time data to test changes on your site or app. For example, you can monitor user responses to design changes, new content, or updated features and make adjustments based on real-time feedback.
- Collaboration:
- Share real-time insights with your team to facilitate quick decision-making and collaborative problem-solving. Real-time data can be particularly useful for marketing, sales, and customer support teams.
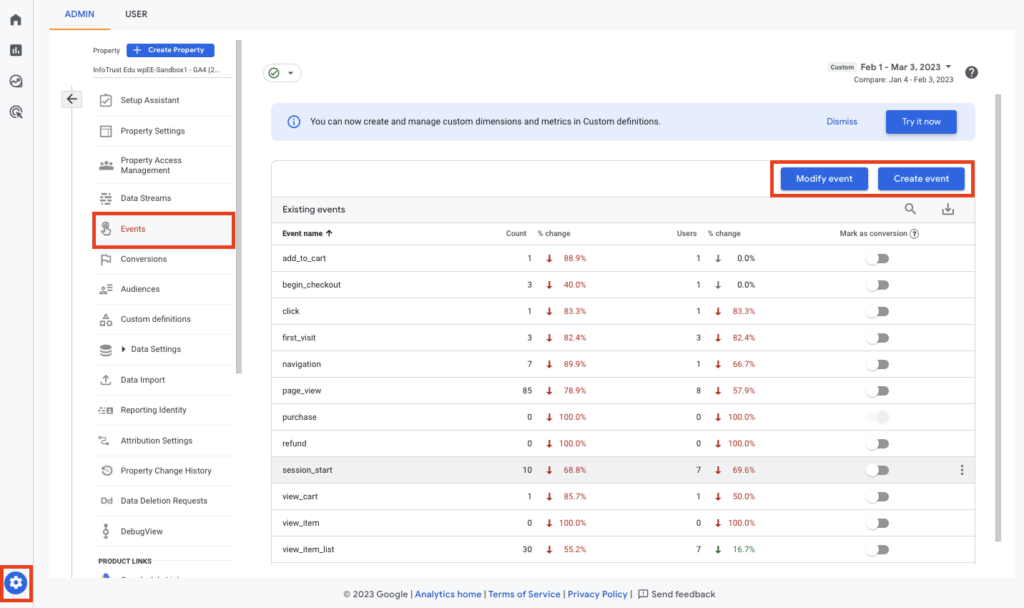
Editing your events in GA4
It will display the default events that come with Google Analytics 4 when you first access the events menu. Additionally, there are buttons at the top of that page that let you create a new event or alter an existing event. Additionally, the menu features simple sliders that can convert any occurrence into a tracked conversion.
Only certain clicks on your website should be considered conversions, even if every user click is significant. Modifying events at that point becomes crucial. You may create brand-new events that track just certain clicks. Click the “create an event” button to get started. Then, you’ll change the event’s name and provide its prerequisites. You may create an event for “page location” and then enter the name of the page you wish to monitor as all page visits in GA4 are regarded as events.
Information derived from:
https://searchengineland.com/google-deprecate-universal-analytics-on-july-1-2023-382648
https://searchengineland.com/how-to-get-started-in-google-analytics-4-344838