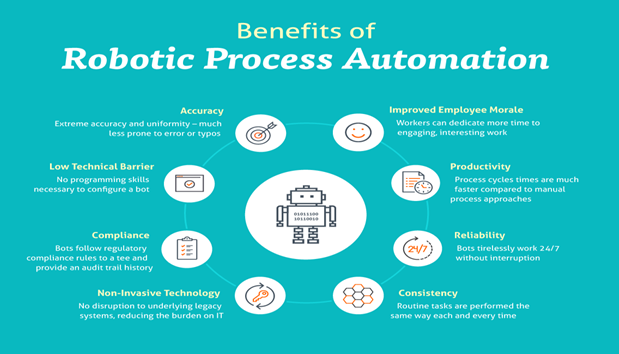
About Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a type of software technology that allows businesses to automate repetitive, rule-based processes through the use of software robots or bots. These bots can interact with digital systems and applications in the same way that a human employee would, making RPA a valuable tool for streamlining business operations and improving efficiency.
One of the key benefits of RPA is that it can automate processes without requiring significant changes to existing systems or processes. Instead, bots can be trained to complete tasks by following a set of rules and guidelines, allowing businesses to automate processes quickly and cost-effectively.
RPA bots can be used to perform a wide range of tasks, including data entry, invoice processing, customer service inquiries, and more. They can be integrated with existing systems and applications, allowing them to interact with other tools and technologies in real-time.
In addition to improving efficiency and reducing costs, RPA can also help businesses to reduce errors and improve accuracy. Because bots are designed to follow strict rules and guidelines, they are less likely to make mistakes or overlook important details. This can help to improve the quality of work and reduce the risk of errors that could have a negative impact on the business.
RPA is a valuable technology that can help businesses to automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks and improve efficiency. By leveraging software robots, businesses can reduce costs, improve accuracy, and focus on more strategic initiatives that drive growth and innovation.
Types of Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that involves the use of software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks. There are three main types of RPA: attended, unattended, and hybrid. Let’s explore each of these types in more detail:
Attended RPA:
Attended RPA is designed to work alongside human workers to automate specific tasks. These robots are deployed on a user’s workstation and are triggered by specific actions such as clicking a button or filling out a form. The robot can then perform the required task, such as filling out a form or processing data. Attended RPA is useful for tasks that require human intervention but are repetitive and time-consuming.
Unattended RPA:
Unattended RPA is designed to run on its own without any human intervention. These robots are deployed on servers or virtual machines and are programmed to perform tasks at specific times or in response to certain events. They can work 24/7, which makes them ideal for tasks that require continuous processing. Unattended RPA is useful for tasks that are highly repetitive and require no human intervention.
Hybrid RPA:
Hybrid RPA is a combination of both attended and unattended RPA. It allows for the automation of both attended and unattended tasks, which provides greater flexibility and efficiency. Hybrid RPA is useful for tasks that require a combination of human and robotic intervention.
Rule-Based Automation:
Rule-based automation is the most basic form of RPA. It involves creating a set of rules that the robot follows to automate a specific task. The robot is programmed to follow a specific sequence of steps, and it can only perform the task that it was designed for. Rule-based automation is useful for tasks that are highly repetitive and follow a specific set of rules.
Cognitive Automation:
Cognitive automation is a type of RPA that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to automate complex tasks. These robots can learn from past experiences and make decisions based on that learning. They can also handle unstructured data, such as emails or text, which makes them useful for tasks that require the processing of large amounts of data. Cognitive automation is useful for tasks that require a high level of decision-making or processing of unstructured data.
Intelligent Automation:
Intelligent automation is a combination of RPA and AI. It combines the rule-based automation of RPA with the decision-making capabilities of AI. These robots can automate complex tasks that require a high level of decision-making and can learn from past experiences. Intelligent automation is useful for tasks that require a combination of human and robotic intervention, and where decisions need to be made based on complex data.
Tools used for Robotic Process Automation
UiPath:
UiPath is one of the most popular RPA tools used by businesses. It allows users to automate tasks by creating workflows that interact with applications through the user interface. UiPath has a drag-and-drop interface that makes it easy to create automation, and it supports a wide range of applications, including web and desktop applications.
Blue Prism:
Blue Prism is another popular RPA tool that is designed for enterprise-level automation. It uses a visual designer to create workflows, and it supports a wide range of applications and technologies, including mainframes and SAP systems. Blue Prism also has a control room that allows users to monitor and manage automation.
Automation Anywhere:
Automation Anywhere is an RPA tool that uses a combination of traditional RPA and cognitive automation to automate complex tasks. It has a drag-and-drop interface that allows users to create bots without coding skills, and it supports a wide range of applications and technologies.
WorkFusion:
WorkFusion is an RPA tool that uses AI and machine learning to automate complex tasks. It has a visual designer that allows users to create bots without coding skills, and it supports a wide range of applications and technologies. WorkFusion also has a control tower that allows users to monitor and manage automations.
Pega:
Pega is an RPA tool that uses AI and machine learning to automate complex tasks. It has a visual designer that allows users to create workflows without coding skills, and it supports a wide range of applications and technologies. Pega also has a control centre that allows users to monitor and manage automations.
Kryon:
Kryon is an RPA tool that uses AI and machine learning to automate complex tasks. It has a visual designer that allows users to create workflows without coding skills, and it supports a wide range of applications and technologies. Kryon also has a control centre that allows users to monitor and manage automations.
WinAutomation:
WinAutomation is an RPA tool that allows users to automate tasks on Windows computers. It has a visual designer that allows users to create workflows without coding skills, and it supports a wide range of Windows applications and technologies.
Skills required for Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves automating repetitive and rule-based tasks using software robots. The demand for RPA is increasing rapidly, and many organizations are adopting this technology to streamline their business operations. To work with RPA, several skills are required. Below are some paragraphs that explain the skills required for Robotic Process Automation:
Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills:
As an RPA developer, you need to have strong analytical and problem-solving skills to understand the business processes and identify the areas that can be automated. You must be able to analyze the data and identify patterns and trends to develop effective automation solutions.
Programming Skills:
RPA requires a good understanding of programming languages such as Java, Python, and C#. You need to be proficient in at least one programming language to develop and maintain the automation scripts. You also need to be familiar with software development tools such as Visual Studio, Eclipse, and IntelliJ IDEA.
Technical Skills:
Along with programming skills, you need to have a good understanding of various technologies such as API, XML, and JSON. You must be familiar with database concepts and should have experience in SQL programming. Knowledge of web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is also essential.
Communication Skills:
As an RPA developer, you need to communicate with various stakeholders, including business analysts, project managers, and end-users. You must be able to understand their requirements and translate them into automation solutions. Good communication skills are essential to effectively communicate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Project Management Skills:
RPA projects involve multiple stakeholders and require effective project management skills. As an RPA developer, you need to be able to manage the project timeline, prioritize tasks, and communicate project status to various stakeholders. You should also be able to identify and mitigate project risks.
Attention to Detail:
RPA involves automating repetitive tasks that require a high level of accuracy. As an RPA developer, you need to have an eye for detail to ensure that the automation scripts are error-free and meet the business requirements.
Continuous Learning:
RPA technology is evolving rapidly, and as an RPA developer, you need to keep yourself updated with the latest tools and technologies. You should be willing to learn new skills and adapt to the changing technology landscape.
Conclusion
Overall, RPA is a valuable tool for organizations looking to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks and improve operational efficiency. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements in its capabilities and wider adoption across different industries. One of the main advantages of RPA is that it can be used to automate processes across different systems and applications, which can be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional automation techniques. RPA also requires minimal coding, which makes it accessible to a wider range of users.
Frequently Asked Questions
RPA bots are programmed to perform a series of actions that mimic human interactions with digital systems and applications. They can navigate through different screens, fill in forms, extract and process data, and perform other tasks based on predefined rules and instructions.
RPA can be used for a wide range of tasks and processes, including data entry, invoice processing, customer service, HR processes, financial operations, supply chain management, and more.
RPA can help organizations to reduce costs, increase efficiency, improve accuracy and consistency, enhance customer experience, and free up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities.
RPA is different from traditional automation because it does not require programming skills or extensive IT expertise to implement and maintain. RPA bots can be trained and configured by business users and can be easily updated and modified as needed.
Some common misconceptions about RPA include that it will replace human workers, that it requires significant investment and IT resources, and that it can only be used for simple and repetitive tasks.
Some key considerations for implementing RPA include identifying the right processes and tasks to automate, ensuring that the organization has the necessary skills and resources to implement and maintain RPA, and developing a governance framework to manage RPA bots and ensure compliance with regulations and policies.
RPA can be secure if proper security measures are implemented, such as access controls, encryption, and monitoring. However, like any technology, RPA can also pose security risks if not properly configured or maintained.
Yes, RPA can be integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing, to enhance its capabilities and automate more complex tasks.
RPA is evolving rapidly, with new capabilities and applications emerging all the time. Some of the latest developments include the integration of cognitive technologies, such as computer vision and natural language processing, and the use of RPA for more strategic and innovative tasks, such as process discovery and optimization.

%20(1).jpg)