Prevent yourself from Cyber Crime
But do the people who send the messages look like that?
The question of whether people who send messages look like their real-world personas is an intriguing one, blending elements of psychology, sociology, and technology. In a world where digital communication has become the norm, it’s essential to explore how accurately these messages reflect the true identities and appearances of the individuals behind them.
Digital Personas and Real-World Identities
The rise of digital communication platforms—social media, emails, messaging apps, and forums—has given people the ability to craft and curate their online personas. These digital identities can often differ significantly from their real-world counterparts. The motivations behind these differences can be manifold:
-
Anonymity and Privacy: Many people value their privacy and choose to remain anonymous or use pseudonyms online. This anonymity allows them to express themselves freely without the fear of judgment or repercussions in their real lives. Consequently, their digital persona might not provide any visual or factual clue about their real appearance or identity.
-
Self-Presentation: Online platforms allow individuals to present themselves in ways they deem most favorable. This can involve sharing selectively edited photos, using avatars, or even creating entirely fictitious identities. The desire to appear more attractive, confident, or socially adept online can lead to a significant disparity between one’s digital and real-world self.
-
Escapism and Fantasy: For some, the digital world offers an escape from the constraints of their real life. They may create and embody personas that reflect their fantasies or idealized versions of themselves. These personas might be radically different in appearance and behavior from their real-life counterparts.
The Psychology of Online Identity
The psychological aspect of online identity formation is critical to understanding why people might present themselves differently online. Factors such as self-esteem, social anxiety, and the need for social validation play significant roles.
-
Self-Esteem and Validation: People with low self-esteem might create more positive and idealized online personas to seek validation and acceptance from their peers. The feedback they receive online can significantly impact their self-worth, leading them to maintain these altered identities.
-
Social Anxiety: Individuals who struggle with face-to-face interactions due to social anxiety may find comfort in the anonymity and control offered by digital communication. They can take their time to craft responses, choose when to interact, and avoid the immediate pressure of real-life social cues.
Technology and Authenticity
Advancements in technology, particularly in the realm of AI and deep learning, have further complicated the relationship between digital personas and real-world identities. Deepfake technology, for example, can create highly realistic but entirely fabricated images and videos of people. This raises ethical concerns about authenticity and trust in digital interactions.
-
Deepfakes and Misrepresentation: The ability to create convincing deepfakes means that visual representations online can no longer be taken at face value. This technology can be used maliciously to impersonate individuals, spreading misinformation and eroding trust in digital content.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These technologies offer new ways for people to present themselves online. Avatars and virtual environments can be customized to an unprecedented degree, allowing individuals to express themselves in ways that might be impossible in the real world.
Social Media and Perception
Social media platforms, where visual content plays a significant role, have a profound impact on how people perceive others and themselves. The constant stream of curated images and posts can create unrealistic expectations and standards.
-
Filters and Editing Tools: The widespread use of filters and photo editing tools means that the images people share online are often enhanced versions of reality. This can lead to distorted perceptions of beauty and normalcy, affecting both the viewers and the content creators.
What should customers do if they fall victim to cyber fraud?
Kaushik recommends that people first freeze their bank accounts and credit cards, then change their online and mobile banking passwords.
“There is a 24-hour window in which they must notify the bank of the cyber-fraud. They should start a legal process to do this in order to reduce the bad effects of cybercrime. Customers who want to file a written complaint against cybercriminals can do so by calling their local cybercrime investigation cell. Or you can do the same thing online,” he said.
So, how can banking customers keep themselves safe?
Kaushik said that you should never open or download an attachment if you don’t know what it is for. Just as important is getting real, licensed antivirus software for all of your devices. People should also avoid clicking on links in emails that look suspicious but claim to have real information, and they shouldn’t share personal information on social media. Users can also stop or get around moving cyber threats by using a VPN service. Even when traveling, you should stay away from free internet or hotspots. To protect network traffic, one should instead use a paid VPN.
Keeping oneself safe in the realm of banking involves a combination of digital vigilance, secure practices, and awareness of potential threats. Here are comprehensive strategies banking customers can adopt to safeguard their financial information and transactions:
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
- Complexity: Create passwords that are at least 12 characters long, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Uniqueness: Avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts. Each banking account should have a unique password.
- Password Managers: Utilize password managers to generate and store complex passwords securely.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Additional Security Layer: 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring not only a password and username but also something that only the user has on them, such as a physical token or a mobile device.
- Authentication Methods: Use authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Authy instead of SMS-based 2FA, which can be more vulnerable to interception.
3. Monitor Your Accounts Regularly
- Frequent Checks: Regularly review bank statements and transaction histories for any unauthorized transactions.
- Alerts and Notifications: Set up account alerts to receive notifications for transactions above a certain amount, failed login attempts, or changes to account information.
4. Be Cautious with Emails and Links
- Phishing Awareness: Be vigilant about phishing emails that appear to be from your bank but are designed to steal your information. Look out for suspicious links, typos, and urgent requests for personal information.
- Verify Contacts: Instead of clicking on links in emails, directly type the bank’s web address into your browser or use their official app.
5. Secure Your Devices
- Antivirus Software: Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices.
- Software Updates: Keep your operating system, browser, and banking apps updated to protect against the latest security vulnerabilities.
- Lock Devices: Use strong passwords, PINs, or biometric locks (fingerprint or facial recognition) to secure your devices.
6. Use Secure Networks
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Refrain from conducting banking transactions over public Wi-Fi networks. Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) if you must access your bank account on a public network.
- Secure Home Network: Ensure your home Wi-Fi network is secured with a strong password and encryption (WPA3 or WPA2).
7. Beware of Social Engineering
- Information Disclosure: Be cautious about the personal information you share online, especially on social media, as it can be used to guess security questions or impersonate you.
- Verification: If someone calls claiming to be from your bank, ask for their credentials and verify by calling the bank directly using a number you know is legitimate.
8. Use Official Banking Apps
- Trusted Sources: Download banking apps only from official app stores (Google Play Store, Apple App Store) and ensure they are published by your bank.
- App Updates: Regularly update your banking apps to benefit from the latest security enhancements.
9. Check for Secure Websites
- HTTPS: Ensure the bank’s website URL begins with “https://” which indicates a secure connection.
- SSL Certificates: Look for a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating that the website uses SSL (Secure Socket Layer) encryption to protect your data.
10. Protect Your Cards and Personal Information
- Card Security: Keep your cards in a safe place and do not share your card details with anyone.
- Shred Documents: Shred any documents containing personal or financial information before disposing of them.
11. Use Biometrics Where Possible
- Enhanced Security: Many banking apps offer biometric authentication such as fingerprint or facial recognition, which provide an additional layer of security beyond passwords.
12. Educate Yourself on Fraud Trends
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on the latest fraud and scam techniques targeting banking customers.
- Bank Resources: Many banks provide resources and tips on how to stay safe; regularly review these materials.
13. Report Suspicious Activity Immediately
- Quick Action: If you suspect any fraudulent activity or if your card is lost or stolen, report it to your bank immediately to minimize potential damage.
- Freezing Accounts: Know how to quickly freeze your accounts through your bank’s app or customer service in case of emergency.
14. Use Secure Payment Methods
- Digital Wallets: Consider using digital wallets (like Apple Pay or Google Wallet) for transactions as they use encryption and tokenization for security.
- Contactless Payments: These are generally more secure than swiping a card, as they do not transmit your actual card number during the transaction.
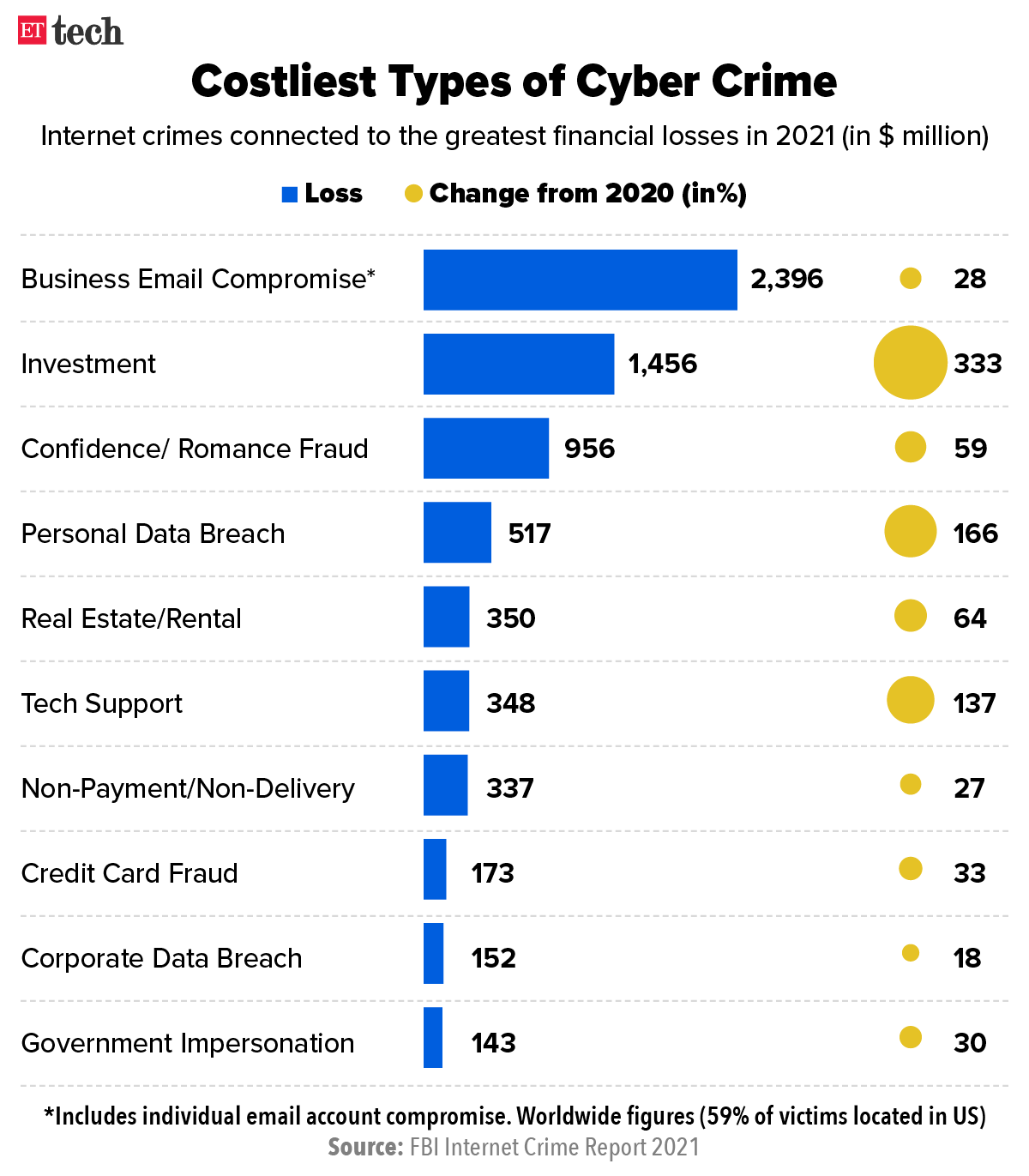
Costliest Types of Cyber Crime
Cybercrime has become a significant threat in the digital age, with some types proving to be particularly costly for individuals, businesses, and even governments. The financial impact of these crimes can be devastating, affecting the global economy and compromising sensitive information. Here are some of the costliest types of cybercrime:
1. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is one of the most financially damaging types of cybercrime. This malware encrypts the victim’s data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid, usually in cryptocurrency to maintain anonymity. The cost includes not only the ransom payment but also the downtime and lost productivity while systems are offline. Additionally, there are expenses related to data recovery, legal fees, and efforts to improve cybersecurity to prevent future attacks. In 2021 alone, global ransomware damage costs were projected to exceed $20 billion.
2. Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Business Email Compromise is a sophisticated scam targeting businesses that regularly perform wire transfers. Cybercriminals gain access to a company’s email accounts, often through phishing attacks, and then deceive employees into transferring large sums of money to fraudulent accounts. BEC scams can result in multi-million dollar losses. According to the FBI, BEC schemes have caused over $26 billion in losses globally from 2016 to 2019.
3. Cryptocurrency Theft
With the rise of digital currencies, cybercriminals have increasingly targeted cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets. These thefts can be particularly costly due to the high value of digital currencies and the irreversibility of transactions. In some cases, hackers have stolen hundreds of millions of dollars in a single breach. For instance, the 2018 Coincheck hack resulted in losses of over $530 million in cryptocurrency.
4. Data Breaches
Data breaches involve unauthorized access to sensitive, protected, or confidential data. This can include personal information, financial data, or intellectual property. The costs associated with data breaches are immense, covering regulatory fines, legal fees, and the expense of notifying affected individuals. Additionally, businesses face reputational damage and loss of customer trust. The 2020 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report estimated the average total cost of a data breach to be $3.86 million.
5. Intellectual Property (IP) Theft
Intellectual property theft involves stealing trade secrets, patented information, or proprietary technologies. This type of cybercrime is particularly damaging to businesses in sectors like technology, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing, where IP is a key competitive advantage. The financial impact includes the loss of revenue, decreased market share, and the cost of litigation to protect intellectual property rights. The Commission on the Theft of American Intellectual Property estimates that IP theft costs the U.S. economy up to $600 billion annually.
6. Financial Fraud
Financial fraud encompasses a range of activities, including identity theft, credit card fraud, and investment scams. Cybercriminals use stolen personal information to access bank accounts, apply for loans, and make unauthorized purchases. The financial impact on individuals and financial institutions is substantial, covering both direct losses and the costs associated with rectifying the fraud, such as credit monitoring services and legal expenses. According to the Federal Trade Commission, U.S. consumers lost over $3.3 billion to fraud in 2020.
Information is derived from:
The Economic Times (https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/tech/technology/business-email-scam-costliest-type-of-us-cybercrime-in-2021-fbi-report/articleshow/92226008.cms)
Cyber-crime prevention in India: Barking up the wrong tree ( https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/blogs/science-nomad/cyber-crime-prevention-in-india-barking-up-the-wrong-tree/ )
Cyber fraud in banking: Key threats and how to overcome them (https://www.cnbctv18.com/personal-finance/cyber-fraud-in-banking-key-threats-you-should-know-and-how-to-overcome-11495322.htm )