Hosting a New site Online or Live
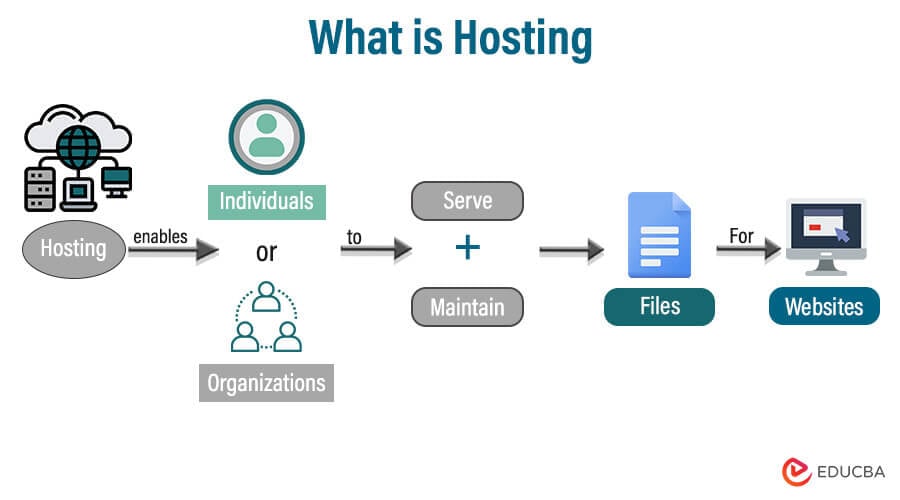
Web hosting is a service that enables the hosting or posting of web-server applications (websites or web pages) on a computer system, enabling web browser clients to easily access electronic material on the Internet.
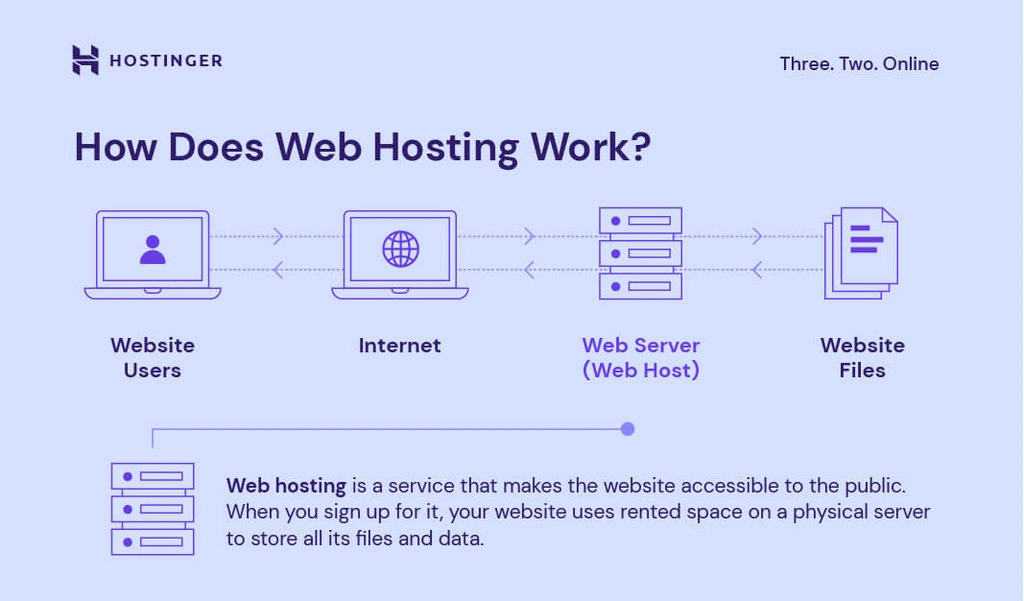
A computer system that offers web hosting is known as a web server or web host. All Internet users need to do to visit your website is enter the domain or address of your website into their browser. The user’s machine will then establish a connection with your server, and their browser will then be used to access your web pages. In essence, web host enables their clients to upload data to a certain kind of computer called a web server, including HTML pages, graphics, and other multimedia files. It offers reliable, fast connections to the Internet’s backbone.
What does hosting a site means?
Hosting a website involves making your website accessible on the internet. This is done by storing the website’s files on a server connected to the internet. When users want to visit your website, they type your website’s address (domain name) into their web browser, which then connects to the server where your website is hosted and delivers the website’s content to their device.
Key Components of Website Hosting
- Web Server: A powerful computer that stores the files of your website, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and videos. It processes requests from users’ browsers and delivers the requested web pages.
- Domain Name: The address of your website that users type into their browser, such as www.example.com. The domain name is linked to the server’s IP address, making it easier for users to access your site.
- Hosting Provider: A company that provides the technology and services needed for the website to be viewed on the internet. They offer space on their servers for storing your website’s files and ensure your site remains accessible.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data that can be transferred between your website and its users. Higher bandwidth allows more users to access your site simultaneously without performance issues.
- Storage: The amount of disk space allocated to your website on the server. This storage is used to hold all the files and databases necessary for your website to function.
Types of Web Hosting
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share the same server and its resources. It is cost-effective and suitable for small to medium-sized websites with moderate traffic. However, performance can be affected by other sites on the same server.
- VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server): A single server is divided into multiple virtual servers, each acting as a dedicated server for a specific user. VPS hosting offers better performance and more control than shared hosting.
- Dedicated Hosting: You rent an entire physical server exclusively for your website. This type provides the highest level of performance, security, and control, suitable for large websites with high traffic volumes.
- Cloud Hosting: Uses a network of interconnected servers to host websites. It offers scalability, as resources can be adjusted based on demand, ensuring consistent performance even during traffic spikes.
- Managed Hosting: A service where the hosting provider takes care of server management, maintenance, security, and backups, allowing you to focus on your website’s content and functionality.
- WordPress Hosting: Specifically optimized for WordPress websites, offering features like one-click WordPress installation, automatic updates, and enhanced security.
Key Features of Web Hosting
- Uptime Guarantee: The percentage of time that the hosting provider guarantees your website will be available. A higher uptime percentage (e.g., 99.9%) indicates better reliability.
- Security: Hosting providers offer various security measures, such as SSL certificates, firewalls, malware scanning, and DDoS protection to safeguard your website.
- Customer Support: Quality of technical support provided by the hosting company, including availability (24/7 support), response time, and support channels (live chat, phone, email).
- Control Panel: A user-friendly interface provided by the hosting company to manage your hosting account, including website files, domains, databases, and email accounts. Common control panels include cPanel and Plesk.
- Scalability: The ability to easily upgrade your hosting plan to accommodate increased traffic and resource needs without experiencing downtime or performance issues.
- Backup Services: Regular backups of your website’s data to prevent data loss in case of server failures, hacking, or accidental deletions.
Steps to Host a Website
- Choose a Hosting Provider: Research and select a hosting provider that meets your needs in terms of performance, features, and budget.
- Select a Hosting Plan: Decide on the type of hosting that suits your website (shared, VPS, dedicated, cloud, managed, or WordPress hosting).
- Register a Domain Name: Purchase a domain name that represents your website. Many hosting providers offer domain registration services.
- Set Up Your Hosting Account: Sign up for a hosting plan and configure your account. This includes setting up your domain, email accounts, and databases if needed.
- Upload Your Website Files: Transfer your website’s files to the server using the hosting provider’s control panel or an FTP client. This includes HTML, CSS, JavaScript files, images, and any other assets.
- Configure Your Website: Set up any necessary databases, configure your website’s settings, and ensure all links and resources are correctly pointed to their respective locations on the server.
- Test Your Website: Before making your site live, test it thoroughly to ensure all pages load correctly, links work, and there are no errors.
- Launch Your Website: Once everything is set up and tested, your website is ready to go live. Share your domain name with your audience and start promoting your site.
Hosting is the process of storing, delivering, and controlling files for one or more Web sites (also known as Web site hosting, Web hosting, and Webhosting). More important than the computer space given for Web site data is a speedy Internet connection. Most hosting companies use T-carrier system lines to provide connectivity. For a single business operating its own website, a similar link would normally be required and expensive. By using a hosting company, many organizations can share the expense of a fast Internet connection for providing data.
Many Internet service providers, including America Online, give customers free hosting for a modest Web site on one of their machines. Users that register on the website Geocities receive an equivalent amount of free web space. These services are not only entirely free but also remarkably straightforward.
Many hosting companies refer to their services as “virtual hosting.”A common implication of virtual hosting is that every website will have its own domain name, set of email addresses, and openness in the services they offer. The terms “virtual hosting” and “hosting” are frequently used synonymously. You can have your own virtual server with some hosting companies, providing the idea that you are in charge of a server that is only used for your website.
The following is a list of various Web hosting service types
-
No-cost hosting
This is a completely free, unpaid web hosting service. This kind of hosting is offered by a lot of well-known websites that let users host a few web pages for free.
Advantages :
- Free of charge
- Websites can be used to post adverts. advertisements in the form of banners and other media
Disadvantages:
- Customer service is lacking
- Lower data transfer rates and low bandwidth
- Unable to control your website
-
Virtual/Shared Hosting:
It is a type of web hosting where numerous websites are housed on a single internet-connected web server. This kind of hosting is offered through a personal website at www.yourname.com.
Advantages:
- Simple and inexpensive
- Secured by the hosting company
- 24/7 technical assistance
Disadvantages:
- Shared resources may cause the entire server to lag
- Less adaptable compared to dedicated hosting
-
Dedicated Hosting :
Large websites with heavy traffic should use this sort of hosting, which is provided by a dedicated server. In this scenario, a hosting firm rents a whole web server to the company that wants to go online. This is appropriate for businesses that manage huge online malls, host larger websites, or administer the websites of others.
Advantages:
- Fantastic for large businesses
- Dependable database support
- Continual software support
- Effective email solutions
- Access to your servers’ full root privileges
Disadvantages:
- It’s pretty pricey
- Better skill sets are necessary
-
Co-located Hosting :
With this hosting, you are able to set up your own web server on a service provider’s property. It is comparable to dedicated hosting with the exception that the user-business now supplies the server and the hosting firm takes care of its physical requirements.
Advantages:
- More Bandwidth and High Uptime
- Numerous Software Alternatives
- Maximum Security
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to set up and troubleshoot
- It’s pricey
- Demand advanced talents
5 Things About Web Hosting You Should Know
Web hosting may be the aspect of the internet that is most undervalued. You can access Netflix content, memes, articles, tweets, websites, online games, and podcasts by visiting servers that someone or a company has paid to maintain. In a nutshell, web hosting is a minor yet crucial aspect of using the internet.
-
The Types of Hosting Differ Significantly
The terms shared, VPS, dedicated, cloud, WordPress, and reseller have probably appeared on a web host’s website if you’ve spent any time there. They represent the numerous types of web hosting even though not every web host offers them all. Furthermore, there are significant variances among the various hosting types.
The least expensive type of web hosting, shared hosting, is provided by almost all web hosts. Your website shares a server and server resources with numerous other websites when you use shared hosting. Shared hosting is the best option if you want to keep your web hosting costs low and don’t anticipate receiving a lot of traffic. Expect to pay less than $10 a month for this kind of site hosting. However, this type of hosting is truly best suited for modestly sized websites with low bandwidth requirements. You should be ready for the occasional slowdown should one of your site-mates start drawing a lot of traffic because you’re sharing resources with other websites. If you’re on a tight budget, free web hosting is an option, but it has its own limitations (typically ads and extremely low server specs).
-
Data Transfer and Bandwidth Are Not the Same
Although the phrases “bandwidth” and “data transfer” are sometimes used synonymously to refer to the volume of data that your website serves to visitors, they actually have different definitions.
While data transfer is the throughput or the real amount of information that can be used over a specific period of time—typically a month—bandwidth reflects the entire amount of data that can be transported at one time. Imagine a web host with a maximum bandwidth of 5GB, but your website may only be able to handle 1GB of data transfers each month, depending on your hosting package.
-
Unlimited Is Not Really Unlimited
Web hosts will seduce you with the promise of limitless storage or monthly data transfers in order to sign up for their web hosting plans. Generally speaking, the deal is not entirely sincere. While I won’t argue that these web servers are outright lying, the claims of “unlimited” storage or data transfers almost always contain restrictions that differ from business to company. For instance, FatCow claims to provide “oodles” of disc space and declares that there is no limit to the amount of content a user may upload—so long as the user complies fully with the terms of service and uses the storage “for the usual operation of your FatCow website.” It is comparable to the bottomless shrimp bar: If a restaurant doesn’t just run out of shrimp first, they’ll eventually have to stop serving you.
Commonly seen on shared or WordPress plans, unlimited storage, and data transfers let you go crazy… within bounds. You’ll be in good standing if your blog receives a consistent flow of respectable traffic (whatever that may entail!). You shouldn’t anticipate being able to upload or stream 50TB of data every day, though. The typical person is probably engaging in some dubious activity instead of doing that.
-
The Solid-State Drive vs. Hard Disk Drive Tradeoff
You’ll probably get space on a conventional hard disc drive (HDD) server if you sign up for shared web hosting. An HDD-based server has the benefit of being able to provide substantial amounts of storage for a reasonable price. Web hosts will give you the choice to create a website on a solid-state drive as you go up the hosting ladder to more potent services, such as VPS and dedicated (SSD).
-
Generally, A Linux Server Will Do
The operating system that runs the servers at almost all web hosts is Linux. Actually, I don’t believe I’ve ever assessed a web host without a free, open-source OS. You can create a website without doing any additional back-end work even if you are unfamiliar with Linux. Building websites is easy thanks to website builders.
However, you must use the Windows Server operating system if your website requires the ASP or ASP.NET scripting frameworks. This is due to the fact that the script you write and the web pages you create can only be used in Windows-based environments.