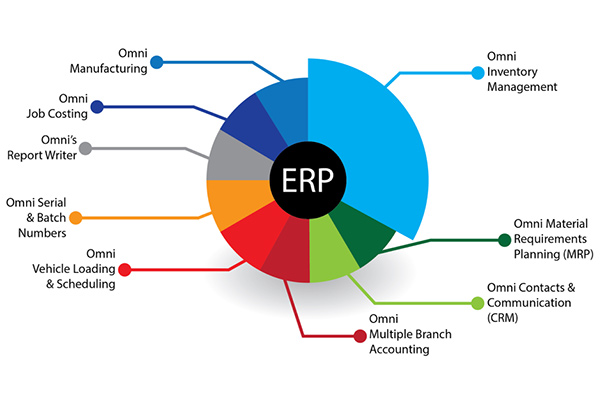
What is meant by ERP (Enterprise resource planning)?
Businesses utilize enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to manage routine tasks like compliance, project management, and supply chain management. A full ERP suite includes business performance management software that aids in planning, budgeting, forecasting, and reporting on an organization’s financial results. Data may be easily exchanged between ERP systems, which link various business activities. ERP systems may collect common transactional data from a variety of sources, reducing the requirement for redundant data and guaranteeing data integrity.
ERP solutions will increase transparency throughout the entire business process by keeping track of all manufacturing, shipping, and financial details. These solutions are available to a wide range of departments and serve as the primary repository for point processes and data within a firm.
In addition to industry-specific modifications, ERP software solutions handle a range of operations in large, semi, and small businesses. ERP systems become an essential tool for companies of all sizes & industries when they are customized to a company’s unique demands.
What functions does ERP software perform?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive system designed to integrate and manage all the essential functions of a business. ERP systems help streamline processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance overall efficiency across various departments. This guide outlines the primary functions of ERP software, highlighting its capabilities and benefits.
Core Functions of ERP Software
1. Financial Management
General Ledger
ERP systems provide a centralized general ledger that consolidates financial data from various departments, ensuring accurate and real-time financial reporting.
Accounts Payable and Receivable
ERP software automates the management of accounts payable and receivable, including invoice processing, payment tracking, and collections.
Budgeting and Forecasting
ERP systems offer tools for budgeting and financial forecasting, helping businesses plan their finances and make informed decisions.
Financial Reporting and Analytics
ERP software generates detailed financial reports and provides analytics tools to monitor financial performance and identify trends.
2. Human Resources Management (HRM)
Employee Data Management
ERP systems store and manage comprehensive employee data, including personal information, job roles, and employment history.
Payroll Management
ERP software automates payroll processing, ensuring accurate and timely payment of salaries, taxes, and other deductions.
Time and Attendance Tracking
ERP systems track employee time and attendance, integrating this data with payroll and HR functions to ensure accurate record-keeping.
Recruitment and Onboarding
ERP software streamlines the recruitment process, from job postings and applicant tracking to onboarding new employees.
Performance Management
ERP systems support performance management by tracking employee goals, performance reviews, and development plans.
3. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Inventory Management
ERP software provides tools for managing inventory levels, tracking stock movements, and optimizing stock replenishment.
Procurement and Supplier Management
ERP systems streamline the procurement process, from purchase requisitions and orders to supplier management and contract tracking.
Order Processing
ERP software automates order processing, ensuring accurate and timely fulfillment of customer orders.
Logistics and Distribution
ERP systems manage logistics and distribution, including warehouse management, shipping, and delivery tracking.
4. Manufacturing and Production Management
Production Planning
ERP software helps with production planning by scheduling manufacturing activities, allocating resources, and managing production timelines.
Bill of Materials (BOM) Management
ERP systems manage the creation and maintenance of bills of materials, ensuring accurate documentation of the components required for production.
Shop Floor Control
ERP software provides tools for monitoring and controlling shop floor activities, including work orders, machine utilization, and production tracking.
Quality Management
ERP systems support quality management by tracking quality control processes, inspections, and compliance with industry standards.
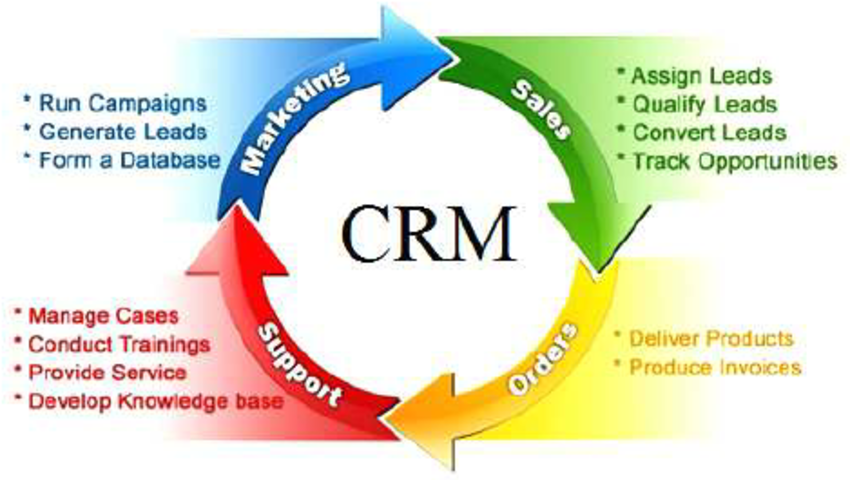
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Data Management
ERP software centralizes customer data, including contact information, purchase history, and interaction records.
Sales Management
ERP systems streamline the sales process, from lead generation and opportunity tracking to order processing and sales reporting.
Marketing Automation
ERP software supports marketing automation by managing campaigns, tracking marketing activities, and analyzing campaign performance.
Customer Service and Support
ERP systems provide tools for managing customer service and support, including ticketing, case management, and service level agreements (SLAs).
6. Project Management
Project Planning and Scheduling
ERP software helps plan and schedule projects, including defining project milestones, tasks, and deadlines.
Resource Allocation
ERP systems manage the allocation of resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials, to ensure optimal project execution.
Time and Expense Tracking
ERP software tracks project-related time and expenses, providing accurate billing and cost management.
Project Reporting and Analytics
ERP systems generate project reports and provide analytics tools to monitor project progress, performance, and profitability.
7. Business Intelligence and Reporting
Data Integration
ERP software integrates data from various departments, providing a unified view of business operations and enabling comprehensive reporting.
Customizable Dashboards
ERP systems offer customizable dashboards that display key performance indicators (KPIs) and real-time data, helping managers make informed decisions.
Advanced Analytics
ERP software provides advanced analytics tools, including data visualization, trend analysis, and predictive analytics, to identify business opportunities and challenges.
8. Compliance and Risk Management
Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems help ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards by automating compliance processes and maintaining accurate records.
Risk Management
ERP software provides tools for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, helping businesses manage potential threats and uncertainties.
Audit Trail
ERP systems maintain a detailed audit trail of all transactions and changes, providing transparency and accountability.
9. Asset Management
Asset Tracking
ERP software tracks the lifecycle of assets, including acquisition, maintenance, and disposal, ensuring accurate asset management.
Maintenance Management
ERP systems schedule and manage preventive and corrective maintenance activities, ensuring optimal asset performance and longevity.
Depreciation Management
ERP software calculates asset depreciation and provides accurate financial reporting for fixed assets.
Benefits of ERP Software
1. Improved Efficiency
Streamlined Processes
ERP systems automate and streamline business processes, reducing manual effort and increasing operational efficiency.
Real-Time Data Access
ERP software provides real-time access to data, enabling quick decision-making and improving responsiveness.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
Centralized Information
ERP systems centralize information, making it easily accessible to all departments and enhancing collaboration.
Integrated Communication
ERP software integrates communication tools, facilitating seamless collaboration and information sharing.
3. Better Decision-Making
Data-Driven Insights
ERP systems provide data-driven insights through advanced analytics and reporting, helping managers make informed decisions.
Predictive Analytics
ERP software offers predictive analytics tools that identify trends and forecast future business performance.
4. Cost Savings
Reduced Operational Costs
ERP systems reduce operational costs by automating processes, optimizing resource utilization, and minimizing errors.
Improved Inventory Management
ERP software improves inventory management, reducing carrying costs and minimizing stockouts and overstock situations.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Scalable Solutions
ERP systems are scalable, accommodating business growth and evolving needs without compromising performance.
Customizable Features
ERP software offers customizable features and modules, allowing businesses to tailor the system to their specific requirements.
-
Accounting management
Initial ERP programs were mostly focused on accounting. Even if there are now more options and features, money management has always been a key component of any ERP system. Your old and new accounting software can be connected with a competent ERP system so you can monitor and track your business’s financial data both immediately and over time. Additionally, it sets up the data so you can dig deeper into it.
-
ERP integration
Despite the wide range of business processes that today’s Erps offer, they still require connectivity & synchronization with the other applications and information sources. With ERP integration, businesses may get a single view of data from several systems, increase the effectiveness of business processes, enhance customer experiences, and make it easier for teams & business partners to collaborate.
-
Administration of human resources
A successful organization operates for reasons other than financial spreadsheets, according to the most successful CEOs & businesspeople. Today’s ERP software enables you to manage your personnel effectively by utilizing the data from your business. You can find your finest employees, recognize achievement, and spot potential HR issues by processing payroll, evaluating performance, and analyzing a range of data.
-
Customer relationship management
The study of client contacts is further aided by corporate resource planning software. Orders may be placed quicker, and you can monitor how fast they are filled. You can monitor each customer’s spending over time to help your salespeople decide where to concentrate their efforts.
-
Controlling the workforce
Similar to a human resource module, an employee management module is designed for businesses that employ more hourly workers than salaried employees. It might keep tabs on an employee’s working hours, attendance, productivity, and frequency of sick days.
-
Controlling the supply chain
A supply chain management module keeps track of each link in the distribution chain, including sub-suppliers, raw material suppliers, distributors, retailers, and customers. It may also deal with materials or goods that have been returned in exchange for a replacement or a refund.
-
Automation of services for experts (Service Resource Management)
A business support automation (PSA) module, also referred to as effective resource management software, allows an organization to plan and manage projects. This module is frequently used by service-based industries. The application allows managers to approve expenses & timesheets. Additionally, it handles both financial and human resources while keeping track of project progress. It streamlines team collaboration by centralizing all crucial papers.
-
Management of orders
Tracking orders from receipt through delivery is the primary function of an order management system. There are several warehouses, distribution centers, and retail outlets where orders may be transferred from clients to be processed and completed before being sent back to the consumer. The order management solution prevents orders from going missing and increases on-time delivery rates, keeping customers satisfied and reducing expedited shipping costs.
Features of ERP
-
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive suite designed to manage and integrate a company’s core business processes. ERP systems streamline and automate various functions, ensuring data accuracy and efficiency across the organization. This guide outlines the primary features of ERP systems, highlighting their capabilities and benefits for businesses of all sizes.
Core Features of ERP Systems
1. Financial Management
General Ledger
ERP systems provide a centralized general ledger that consolidates financial data from various departments, ensuring accurate and real-time financial reporting.
Accounts Payable and Receivable
ERP software automates the management of accounts payable and receivable, including invoice processing, payment tracking, and collections.
Budgeting and Forecasting
ERP systems offer tools for budgeting and financial forecasting, helping businesses plan their finances and make informed decisions.
Financial Reporting and Analytics
ERP software generates detailed financial reports and provides analytics tools to monitor financial performance and identify trends.
2. Human Resources Management (HRM)
Employee Data Management
ERP systems store and manage comprehensive employee data, including personal information, job roles, and employment history.
Payroll Management
ERP software automates payroll processing, ensuring accurate and timely payment of salaries, taxes, and other deductions.
Time and Attendance Tracking
ERP systems track employee time and attendance, integrating this data with payroll and HR functions to ensure accurate record-keeping.
Recruitment and Onboarding
ERP software streamlines the recruitment process, from job postings and applicant tracking to onboarding new employees.
Performance Management
ERP systems support performance management by tracking employee goals, performance reviews, and development plans.
3. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Inventory Management
ERP software provides tools for managing inventory levels, tracking stock movements, and optimizing stock replenishment.
Procurement and Supplier Management
ERP systems streamline the procurement process, from purchase requisitions and orders to supplier management and contract tracking.
Order Processing
ERP software automates order processing, ensuring accurate and timely fulfillment of customer orders.
Logistics and Distribution
ERP systems manage logistics and distribution, including warehouse management, shipping, and delivery tracking.
4. Manufacturing and Production Management
Production Planning
ERP software helps with production planning by scheduling manufacturing activities, allocating resources, and managing production timelines.
Bill of Materials (BOM) Management
ERP systems manage the creation and maintenance of bills of materials, ensuring accurate documentation of the components required for production.
Shop Floor Control
ERP software provides tools for monitoring and controlling shop floor activities, including work orders, machine utilization, and production tracking.
Quality Management
ERP systems support quality management by tracking quality control processes, inspections, and compliance with industry standards.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Data Management
ERP software centralizes customer data, including contact information, purchase history, and interaction records.
Sales Management
ERP systems streamline the sales process, from lead generation and opportunity tracking to order processing and sales reporting.
Marketing Automation
ERP software supports marketing automation by managing campaigns, tracking marketing activities, and analyzing campaign performance.
Customer Service and Support
ERP systems provide tools for managing customer service and support, including ticketing, case management, and service level agreements (SLAs).
6. Project Management
Project Planning and Scheduling
ERP software helps plan and schedule projects, including defining project milestones, tasks, and deadlines.
Resource Allocation
ERP systems manage the allocation of resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials, to ensure optimal project execution.
Time and Expense Tracking
ERP software tracks project-related time and expenses, providing accurate billing and cost management.
Project Reporting and Analytics
ERP systems generate project reports and provide analytics tools to monitor project progress, performance, and profitability.
7. Business Intelligence and Reporting
Data Integration
ERP software integrates data from various departments, providing a unified view of business operations and enabling comprehensive reporting.
Customizable Dashboards
ERP systems offer customizable dashboards that display key performance indicators (KPIs) and real-time data, helping managers make informed decisions.
Advanced Analytics
ERP software provides advanced analytics tools, including data visualization, trend analysis, and predictive analytics, to identify business opportunities and challenges.
8. Compliance and Risk Management
Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems help ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards by automating compliance processes and maintaining accurate records.
Risk Management
ERP software provides tools for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, helping businesses manage potential threats and uncertainties.
Audit Trail
ERP systems maintain a detailed audit trail of all transactions and changes, providing transparency and accountability.
9. Asset Management
Asset Tracking
ERP software tracks the lifecycle of assets, including acquisition, maintenance, and disposal, ensuring accurate asset management.
Maintenance Management
ERP systems schedule and manage preventive and corrective maintenance activities, ensuring optimal asset performance and longevity.
Depreciation Management
ERP software calculates asset depreciation and provides accurate financial reporting for fixed assets.
Benefits of ERP Systems
1. Improved Efficiency
Streamlined Processes
ERP systems automate and streamline business processes, reducing manual effort and increasing operational efficiency.
Real-Time Data Access
ERP software provides real-time access to data, enabling quick decision-making and improving responsiveness.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
Centralized Information
ERP systems centralize information, making it easily accessible to all departments and enhancing collaboration.
Integrated Communication
ERP software integrates communication tools, facilitating seamless collaboration and information sharing.
3. Better Decision-Making
Data-Driven Insights
ERP systems provide data-driven insights through advanced analytics and reporting, helping managers make informed decisions.
Predictive Analytics
ERP software offers predictive analytics tools that identify trends and forecast future business performance.
4. Cost Savings
Reduced Operational Costs
ERP systems reduce operational costs by automating processes, optimizing resource utilization, and minimizing errors.
Improved Inventory Management
ERP software improves inventory management, reducing carrying costs and minimizing stockouts and overstock situations.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Scalable Solutions
ERP systems are scalable, accommodating business growth and evolving needs without compromising performance.
Customizable Features
ERP software offers customizable features and modules, allowing businesses to tailor the system to their specific requirements.
-
Automation
An ERP system can be used to automate tasks like payroll, order fulfillment, invoicing, reporting, and other repetitive business procedures. Automation expedites data entry, reduces mistake rates, and frees up staff time for more valuable activities. Because of how ERP systems work, data entered by one user is visible to all users within the organization. So, for example, an inventory tracking module may immediately start a shipment and invoice when a specific SKU becomes available.
-
Integration
Data silos result in inefficiency, missed opportunities, and departments that operate in conflict with one another. The main, and possibly most important, the advantage of ERP is a centralized view of crucial financial, operational, & business data that may be disseminated in almost real-time throughout the firm.
-
Management of customer relationships
You may keep client data, including contact information, order history, private details, purchase orders, or billing information in one place thanks to the integration between ERP and CRM technologies. When processing shipments, you can access billing data and client addresses thanks to an integrated CRM.
-
Analysis of data
An ERP system gathers & processes data from various company operations, so it makes sense to use analysis to make the most of that data. Simply said, this ERP software function analyses your processes for trends and patterns to assess task efficacy and generate projections for upcoming business choices.
-
Marketing and sales
The ability to sell, upsell, create bids and buy orders, predict, manage commissions, and keep track of crucial information like profit margins & ratios is another advantage that ERP systems that integrated CRM provide to marketing and sales teams.
-
Financial administration
Planning, arranging, and choosing how to use the money most effectively for a firm are all part of the difficult work of financial management. To make judgments about things like capital projects, sources of funding, cash management, and financial controls, for example, financial leaders must monitor and then use financial information from all departments.
-
People resources (HR)
An ERP system’s HR component serves as an all-inclusive platform for employee administration, taking care of timekeeping, payroll, hiring, and onboarding. With ERP integration, complex HR tasks like benefits and tax deductions can be automated, saving time, money, and human error.
-
Manufacturing
ERP’s foundational role has been manufacturing. Today’s systems enhance manufacturing processes by assisting with product planning, raw material sourcing, production monitoring, and forecasting. Additional components include modules for managing work orders, bills of materials, distribution planning, shop-floor control, and product tracking.
Top ERP software
Enterprise Resource Management (ERM) software is a group of ERM solutions. The procedure involves gathering and organizing corporate data with the aid of an interconnected software system.
-
Systems DEAR
It’s a company that creates and markets products. Small to mid-sized manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and e-commerce companies are the target market for this cloud-based ERP solution. Dear Systems is indeed a comprehensive system that contains modules for sales, accounting, production, e-commerce, purchasing, and more. Businesses could use DEAR inventory to create plans for and keep track of each step in the purchasing process.
-
SAP
Businesses can organize their finances, human resources, logistics, and other company processes with the help of SAP (Systems, Applications, & Products in Information Processing), which offers them powerful capabilities. Located in Waldorf, SAP is a business in Europe. It creates business software to aid organizations in making management chores simpler. The world of SAP began 40 years ago.
-
Dynamics X by Microsoft
It is software for managing businesses.
Microsoft, a leader in computer technology and software was established in New Mexico in 1975 and now provides businesses and individuals all over the world with a range of Windows PC software offline services. In addition to creating software for sales and marketing, MS Dynamics also creates solutions for other business functions like ERP, finance, & supply chain management.
-
Netsuite
With the intention of providing companies solutions that integrated customer interactions, ERP, & inventory management into a single platform, Netsuite was established in 2007. It concerns the contribution of the ERP software sector to software as a service. The functionality of standard accounting software is increased by Netsuite ERP.
Conclusion
It might make keeping tabs on travel-related costs and payments easier. ERP may also monitor the status of employees’ training. Whenever it comes to the installation of ERP, there are just as many potential pitfalls as there are potential benefits. However, it appears that whether a project was finished on schedule and within budget often determines whether it was successful. It appears that the opportunity to fully utilize technology to enhance company processes is being overlooked. In order for organizations to more clearly understand how Enterprise Resource Planning benefits them, performance measures must be created and defined.
Frequently Asked Questions
The implementation lifespan outlines the steps involved in implementing an ERP system from beginning to end. Noting this is important.
Most suppliers give some form of training program to assist customers in using the ERP. For instance, Oracle University provides a comprehensive certification and training program that divides Oracle’s ERP’s features and functionality into separate courses.
The process for implementing ERP varies greatly, and there are many alternatives for the way it will be rolled out and who will be affected.
Yes, Exactly trains your workers as a required component of the implementation technique. We can also train your new employee and show him how to utilize the system efficiently for your business goals if a trained workforce leaves and you hire someone else.