Connectivity Cloud
The Connectivity Cloud is a paradigm that encompasses the integration of cloud computing and connectivity technologies. It brings together the power of the cloud, which enables remote data storage, processing, and access, with the pervasive nature of connectivity, which enables the interconnection of devices, sensors, and systems. This synergy empowers users to access and control data and services from anywhere, at any time, using a variety of devices, thereby fostering a seamless and interconnected digital ecosystem.
Introduction
The term “Connectivity Cloud” refers to a comprehensive and integrated suite of cloud-based services designed to enhance and streamline digital connectivity across various devices, platforms, and networks. It leverages cloud computing to offer scalable, flexible, and reliable connectivity solutions, enabling seamless communication, data exchange, and interaction among a multitude of systems and users. This guide delves into the concept of Connectivity Cloud, its components, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding Connectivity Cloud
What is Connectivity Cloud?
Connectivity Cloud encompasses a range of cloud services aimed at ensuring efficient and continuous connectivity. It integrates various connectivity solutions such as IoT (Internet of Things), 5G, edge computing, and cloud networking to provide a unified platform for managing and optimizing digital interactions.
Components of Connectivity Cloud
- IoT Connectivity
- Cloud Networking
- 5G Integration
- Edge Computing
- Unified Communication and Collaboration
- Security and Compliance
1. IoT Connectivity
Overview
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data with each other. Connectivity Cloud enhances IoT by providing a scalable and secure platform for managing these connections.
Key Features
- Device Management: Centralized control and monitoring of IoT devices.
- Data Integration: Seamless integration of data from various IoT sensors and devices.
- Scalability: Ability to handle a growing number of connected devices.
- Security: Robust security measures to protect data and devices from cyber threats.
Applications
- Smart Homes: Integration of devices like smart thermostats, lights, and security systems.
- Industrial IoT: Monitoring and managing industrial equipment and processes.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring and smart medical devices.
2. Cloud Networking
Overview
Cloud networking involves using cloud-based services to manage and optimize network resources and connectivity. It enables organizations to scale their network infrastructure easily and cost-effectively.
Key Features
- Network Management: Centralized management of network resources.
- Scalability: Ability to scale network resources up or down based on demand.
- Performance Optimization: Tools to optimize network performance and reduce latency.
- Security: Advanced security features to protect network data and resources.
Applications
- Corporate Networks: Managing internal and external network resources.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Efficiently delivering digital content to users worldwide.
- Hybrid Cloud Environments: Integrating on-premises and cloud-based network resources.
3. 5G Integration
Overview
5G, the fifth generation of mobile networks, offers high-speed, low-latency connectivity. Integrating 5G with Connectivity Cloud enhances mobile connectivity and supports the growing demand for data-intensive applications.
Key Features
- High Speed: Significantly faster data transfer rates compared to previous generations.
- Low Latency: Reduced delay in data transmission, critical for real-time applications.
- Massive Connectivity: Support for a large number of connected devices.
- Reliability: Improved network reliability and availability.
Applications
- Smart Cities: Real-time monitoring and management of urban infrastructure.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Enabling communication between vehicles and infrastructure.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Supporting immersive experiences with minimal latency.
4. Edge Computing
Overview
Edge computing involves processing data closer to its source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This approach reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing the overall performance of connected systems.
Key Features
- Data Processing: Local processing of data to reduce latency.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Reducing the amount of data transmitted to central servers.
- Scalability: Ability to deploy edge computing resources as needed.
- Security: Enhanced data security by keeping sensitive information local.
Applications
- IoT Devices: Local processing of data from IoT sensors and devices.
- Industrial Automation: Real-time processing of data in manufacturing and production environments.
- Healthcare: Local analysis of medical data for faster diagnosis and treatment.
5. Unified Communication and Collaboration
Overview
Unified communication and collaboration tools integrate various communication channels and platforms into a single, cohesive system. This ensures seamless interaction and collaboration among users, regardless of their location.
Key Features
- Integration: Combining voice, video, messaging, and collaboration tools.
- Accessibility: Ensuring users can communicate and collaborate from any device.
- Scalability: Supporting a growing number of users and communication channels.
- Security: Protecting communication data with encryption and other security measures.
Applications
- Remote Work: Enabling efficient communication and collaboration for remote teams.
- Customer Support: Providing integrated communication channels for customer service.
- Education: Supporting online learning and virtual classrooms.
Evolution
The concept of the Connectivity Cloud has evolved significantly over the years. It can be traced back to the early days of the Internet when the World Wide Web emerged as a global platform for information sharing. However, it was the advent of cloud computing that laid the foundation for the modern Connectivity Cloud. As cloud services became more widespread and affordable, organizations began shifting their data and applications to the cloud, paving the way for unprecedented levels of connectivity.
Key Components
The Connectivity Cloud comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in its functionality:
- Cloud Computing: This is the backbone of the Connectivity Cloud. Cloud computing provides the infrastructure, platforms, and software services needed to host and deliver data and applications over the Internet. Popular cloud service providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Connectivity Technologies: This includes wired and wireless technologies that enable devices and systems to connect to the cloud. Notable examples are Wi-Fi, cellular networks (4G, 5G), satellite communications, and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies.
- IoT Devices: The proliferation of IoT devices, such as smart sensors and connected appliances, plays a crucial role in the Connectivity Cloud. These devices collect and transmit data to the cloud, facilitating real-time monitoring and control.
- Data Storage and Processing: The cloud provides vast storage and processing capabilities, making it possible to store, analyze, and manipulate large datasets. This is essential for applications like data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.
- Security Protocols: Security is paramount in the Connectivity Cloud. Encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms are deployed to protect data and prevent unauthorized access.
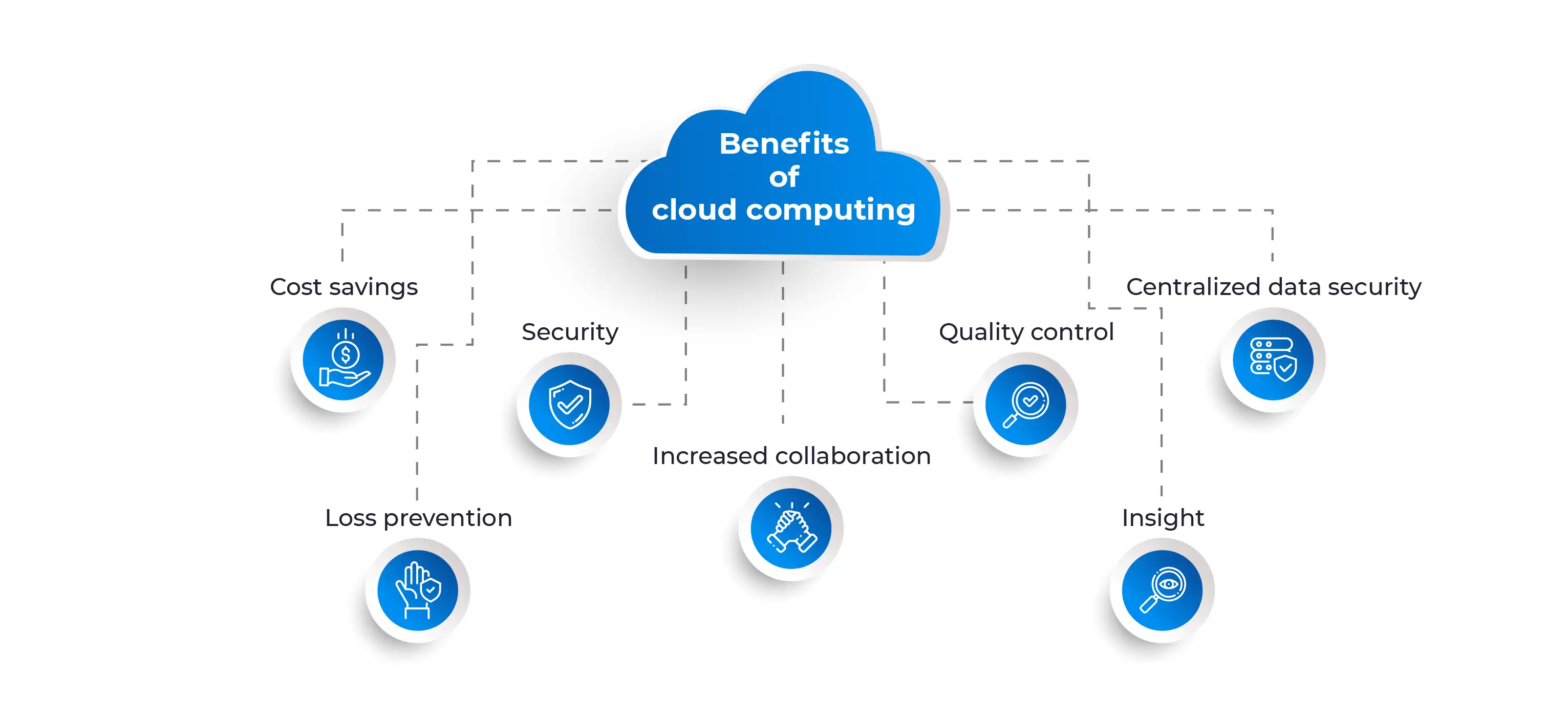
Benefits of the Connectivity Cloud
- Enhanced Communication
One of the primary advantages of the Connectivity Cloud is its ability to facilitate seamless and efficient communication. Whether it’s video conferencing, instant messaging, or collaboration tools, the Connectivity Cloud enables individuals and organizations to connect and collaborate in real-time, regardless of geographical barriers. This has been particularly valuable in an era marked by remote work and global business operations.
- Scalability
The cloud’s scalability is a boon for businesses of all sizes. The Connectivity Cloud allows organizations to scale their resources up or down based on demand. This elasticity is particularly advantageous for startups and growing businesses, as they can avoid costly upfront investments in infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency
The Connectivity Cloud offers significant cost savings. By outsourcing infrastructure and maintenance to cloud providers, organizations can reduce operational costs associated with hardware, data centers, and IT staff. Pay-as-you-go models ensure that organizations only pay for the resources they consume, making it an economical choice.
- Flexibility
The Connectivity Cloud provides unparalleled flexibility. Users can access their data and applications from various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and computers. This flexibility empowers individuals to work and collaborate from virtually anywhere.
- Improved Accessibility
Accessibility is a critical aspect of the Connectivity Cloud. The ability to access data and services from any location with an internet connection is a game-changer. It allows for remote learning, telemedicine, and remote monitoring of assets and systems.
- Data Analytics
The Connectivity Cloud also enables data analytics on a massive scale. Organizations can harness the power of big data to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency. This data-driven decision-making has a profound impact on various industries, from e-commerce to healthcare.
Features
Sure, let’s delve into the features of Connectivity Cloud in more detail. Here are the key features that make Connectivity Cloud a powerful tool for enhancing digital connectivity:
Key Features of Connectivity Cloud
1. IoT Connectivity
Overview:
The Internet of Things (IoT) involves connecting various devices to the internet to enable data exchange and communication. Connectivity Cloud enhances IoT by providing a scalable and secure platform for managing these connections.
Key Features:
- Device Management: Centralized control and monitoring of IoT devices, allowing for easy updates, troubleshooting, and configuration.
- Data Integration: Seamless integration of data from various IoT sensors and devices, enabling comprehensive data analysis and insights.
- Scalability: Capability to handle a growing number of connected devices without compromising performance.
- Security: Robust security measures, including encryption and authentication, to protect data and devices from cyber threats.
2. Cloud Networking
Overview:
Cloud networking involves managing and optimizing network resources and connectivity using cloud-based services. It offers flexibility and scalability for network infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Network Management: Centralized management of network resources, simplifying configuration and maintenance.
- Scalability: Ability to scale network resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Performance Optimization: Tools to optimize network performance, reduce latency, and enhance user experience.
- Security: Advanced security features, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to protect network data and resources.
3. 5G Integration
Overview:
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks, providing high-speed, low-latency connectivity. Integration with Connectivity Cloud enhances mobile connectivity and supports data-intensive applications.
Key Features:
- High Speed: Faster data transfer rates, supporting applications that require high bandwidth.
- Low Latency: Reduced delay in data transmission, crucial for real-time applications like gaming and autonomous vehicles.
- Massive Connectivity: Support for a large number of connected devices, essential for IoT and smart cities.
- Reliability: Improved network reliability and availability, ensuring consistent connectivity.
4. Edge Computing
Overview:
Edge computing involves processing data closer to its source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing performance.
Key Features:
- Data Processing: Local processing of data to reduce latency and improve response times.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Reducing the amount of data transmitted to central servers, optimizing bandwidth usage.
- Scalability: Ability to deploy edge computing resources as needed, ensuring flexible and efficient data processing.
- Security: Enhanced data security by keeping sensitive information local, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
5. Unified Communication and Collaboration
Overview:
Unified communication and collaboration tools integrate various communication channels and platforms into a single system. This ensures seamless interaction and collaboration among users.
- Scalability:
The Connectivity Cloud is built to grow or shrink according to the user’s needs. Whether you’re a small startup experiencing rapid growth or a large corporation with varying demands, this system allows you to easily add or remove devices, resources, or services to accommodate these changing requirements. This flexibility ensures that your network can adapt to evolving business demands without major disruptions.
- Accessibility:
Unlike traditional networking solutions that often require a physical presence in a specific location, the Connectivity Cloud enables users to access resources and services from anywhere as long as they have an internet connection. This accessibility has transformed the way businesses operate by promoting remote work and global collaboration. Users can access the network and its services from virtually any location, fostering flexibility and efficiency.
- Security:
In the age of digital threats and data breaches, security is a paramount concern. The Connectivity Cloud provides advanced security measures to protect your data and connections. It incorporates features such as data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and robust access control mechanisms to ensure that your data remains secure and private. This safeguards your network and prevents unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Reliability:
The Connectivity Cloud is engineered for high availability and reliability. It employs redundant systems, failover mechanisms, and load balancing to ensure that your network connections remain stable, even during periods of high demand or in the event of hardware or software failures. This guarantees that your business operations can continue without disruptions.
- Interoperability:
Interoperability is a key concept that allows different devices, protocols, and systems to work together seamlessly. The Connectivity Cloud promotes this by facilitating the integration of diverse technologies. This means that various devices and systems can communicate effectively, which encourages innovation and collaboration. It eliminates the barriers that can arise from different technologies not being able to work together, leading to a more efficient and interconnected network.
- Flexibility:
Users of the Connectivity Cloud have the flexibility to tailor their network and resource configurations to their specific needs. This customization ensures that they only pay for the resources and services they actually use, helping to optimize costs and resource allocation. It empowers users to adapt their network to their unique requirements, making it a cost-effective and efficient solution.
Use Cases of the Connectivity Cloud
- Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, the Connectivity Cloud is revolutionizing patient care. Remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and electronic health records (EHR) systems are made possible through this technology. Patients can consult with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes, and medical data can be seamlessly shared and accessed by authorized parties, leading to improved patient outcomes and streamlined healthcare delivery.
- Smart Cities
Smart cities leverage the Connectivity Cloud to enhance urban living. From smart traffic management systems to waste management, these cities use real-time data and IoT devices to optimize services and resources. Smart streetlights, parking systems, and public safety solutions are examples of how connectivity is making cities more efficient and sustainable.
- Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, relies heavily on the Connectivity Cloud. Manufacturing processes are becoming more efficient and automated, with the help of IoT sensors, cloud-based analytics, and real-time monitoring. This leads to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and enhanced product quality.
- Education
The Connectivity Cloud has transformed education, especially in remote and hybrid learning environments. Virtual classrooms, online resources, and cloud-based learning management systems enable students and educators to interact and access educational materials from anywhere. This has proven crucial during periods of lockdowns and social distancing.
- Entertainment
The entertainment industry benefits greatly from the Connectivity Cloud. Streaming services, online gaming platforms, and content distribution networks rely on cloud infrastructure to deliver high-quality experiences to users worldwide. The ability to stream movies, play games, and share content seamlessly depends on the speed and reliability of connectivity.
- Finance
In the financial sector, the Connectivity Cloud enhances the accessibility of banking and investment services. Customers can manage their finances, make transactions, and access financial data securely through web and mobile applications. Real-time trading, analytics, and fraud detection also rely on this technology.
Challenges and Concerns
- Security and Privacy
The Connectivity Cloud has raised significant concerns about data security and privacy. Storing sensitive information in the cloud makes it vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches. To mitigate these risks, robust security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems, are essential.
- Reliability
Reliability is another concern, as the uptime of cloud services can affect business operations. Downtime or service interruptions can lead to financial losses and hinder productivity. To address this issue, organizations often employ redundancy and disaster recovery solutions.
- Connectivity Gaps
Not all regions have equal access to high-speed internet, creating digital divides. Connectivity gaps can limit the potential of the Connectivity Cloud, particularly in rural or underserved areas. Bridging these gaps is essential to ensure equitable access to its benefits.
- Regulatory Issues
Different countries have varying regulations and data sovereignty requirements. This can complicate data management and compliance for multinational organizations. Navigating these regulatory challenges is an ongoing concern.
- Data Management
Managing vast amounts of data in the Connectivity Cloud can be complex. Ensuring data integrity, availability, and compliance with data protection regulations is a significant challenge. Data management strategies, including data governance and lifecycle management, are crucial to address these concerns.
The Future of the Connectivity Cloud
- Edge Computing
Edge computing, which brings data processing closer to the data source, is set to play a pivotal role in the future of the Connectivity Cloud. This approach reduces latency, making real-time applications more responsive and efficient.
- 5G Integration
The deployment of 5G networks will further enhance the Connectivity Cloud by providing faster and more reliable connectivity. It will enable new applications, such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery.
- Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) will continue to be integrated with the Connectivity Cloud. AI-powered analytics and automation will optimize processes, enhance personalization, and improve security.
- Quantum Computing
Quantum computing, with its incredible processing power, has the potential to revolutionize the Connectivity Cloud. It will enable more complex simulations, advanced cryptography, and the analysis of vast datasets.
- Sustainable Connectivity
The future of the Connectivity Cloud also includes a focus on sustainability. Green data centers, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient hardware will be essential to reduce the environmental impact of cloud computing and connectivity technologies.
Conclusion
The Connectivity Cloud is a transformative force that is reshaping the way we interact, work, and live. Its ability to connect people, devices, and data across vast distances has opened up endless possibilities. However, it also presents challenges that must be addressed, such as security, reliability, and regulatory compliance.
As the Connectivity Cloud continues to evolve, it will be driven by technological advancements like edge computing, 5G, AI, and quantum computing. Additionally, a focus on sustainability and equitable access will be crucial for its long-term success.
The Connectivity Cloud will not only redefine industries and business models but also have a profound impact on society as a whole. It is a concept that will continue to shape our digital future and influence the way we connect and communicate in an increasingly interconnected world.