About Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that records transactions in a decentralized and secure manner. It is a database that is distributed across a network of computers, where each computer stores a copy of the database. This database consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. These transactions are validated and added to the block by a network of users called nodes or miners. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted, making the blockchain an immutable and transparent record of all transactions that have occurred on the network.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its security. The blockchain is secured by cryptographic algorithms that make it virtually impossible to alter the data stored on it. This makes it an ideal platform for applications that require high levels of security, such as financial transactions, supply chain management, and identity verification.
Another important feature of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases that are centralized and controlled by a single entity, the blockchain is distributed across a network of computers. This means that there is no single point of failure or control, making it more resistant to hacking and censorship.
One of the most well-known applications of blockchain technology is cryptocurrency. Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, was created using blockchain technology. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that are designed to work as a medium of exchange, using cryptography to secure transactions and to control the creation of new units. Other applications of blockchain technology include smart contracts, decentralized finance, and decentralized applications.
Blockchain technology is a decentralized and secure database that stores information in a tamper-proof and transparent manner. It has the potential to revolutionize many industries by enabling secure and efficient transactions, without the need for intermediaries or centralized authorities. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that we will see even more innovative applications of blockchain technology in the future.
How Blockchain Technology Works
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention due to its role in powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as its potential to revolutionize various industries through its unique approach to data management and security. At its core, blockchain technology offers a decentralized, transparent, and secure method of recording transactions and managing data. This article explores how blockchain technology works, its key components, and its applications.
1. What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority, a blockchain operates as a distributed ledger where each participant has access to the entire record of transactions. This decentralized approach enhances security, transparency, and trust among participants.
2. Key Components of Blockchain
a. Blocks
A blockchain is composed of a series of blocks, each containing a set of transactions. Each block includes:
- Transaction Data: Details of the transactions that have occurred.
- Timestamp: The date and time when the block was created.
- Previous Block Hash: A unique identifier (hash) of the preceding block, linking the blocks together.
- Nonce: A random number used in the mining process to create a valid hash.
b. Chains
Blocks are linked together in chronological order to form a chain. Each block contains a reference (hash) to the previous block, creating a continuous chain from the first block (genesis block) to the most recent block.
c. Decentralized Network
Blockchain operates on a decentralized network of computers (nodes). Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain and participates in validating and recording new transactions. This decentralization eliminates the need for a central authority and enhances the resilience of the system.
d. Hash Functions
Hash functions are cryptographic algorithms used to generate a unique fixed-size hash (string of characters) for each block. This hash represents the block’s content and is used to ensure data integrity. A slight change in the block’s data will result in a completely different hash, making it easy to detect tampering.
e. Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are protocols used to achieve agreement among nodes on the validity of transactions. Common consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. The first miner to solve the puzzle adds the block to the blockchain and is rewarded.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Coin holders vote for a small number of delegates who are responsible for validating transactions and creating blocks.
3. How Blockchain Works
a. Transaction Initiation
A transaction is initiated by a user who wants to transfer assets or data. This transaction includes details such as the sender’s and receiver’s addresses and the amount being transferred.
b. Transaction Verification
The transaction is broadcasted to the network of nodes. Nodes validate the transaction based on predefined rules, such as verifying the authenticity of digital signatures and ensuring that the sender has sufficient funds.
c. Block Creation
Once validated, the transaction is bundled with other transactions into a block. Miners (in PoW) or validators (in PoS) work to create a valid block by solving cryptographic puzzles or proving their stake.
d. Block Addition
The newly created block is added to the blockchain. Each block includes a reference to the previous block, linking them together and forming a continuous chain. This addition is verified by the network, ensuring that all nodes agree on the new block’s validity.
e. Ledger Update
All nodes update their copies of the blockchain to include the new block. This ensures that every participant has an identical and up-to-date record of the blockchain.
f. Confirmation
The transaction is considered confirmed once the block containing it is added to the blockchain. Additional confirmations are achieved as more blocks are added on top of the block containing the transaction, enhancing its immutability.
4. Benefits of Blockchain Technology
a. Security
Blockchain technology provides robust security through cryptographic techniques and decentralized consensus mechanisms. The immutable nature of blockchain ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without detection.
b. Transparency
Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network. This transparency fosters trust and accountability, as all transactions can be independently verified.
c. Decentralization
The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of single points of failure and increasing the system’s resilience against attacks and fraud.
d. Efficiency
Blockchain technology can streamline processes by reducing the need for intermediaries and automating transactions through smart contracts. This can lead to faster and more cost-effective operations.
5. Applications of Blockchain Technology
a. Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain is cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital currencies use blockchain technology to enable secure, transparent, and decentralized financial transactions.
b. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency by providing real-time tracking of goods from production to delivery. It helps verify the authenticity of products and prevent fraud.
c. Healthcare
Blockchain technology can improve healthcare data management by securely storing patient records, ensuring data integrity, and enabling seamless sharing of information among healthcare providers.
d. Voting Systems
Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, reducing the risk of tampering and ensuring the integrity of the electoral process.
e. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions written in code. They automatically execute and enforce agreements when conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries.
6. Challenges and Future Directions
While blockchain technology offers many benefits, it also faces challenges such as scalability, energy consumption (especially in PoW systems), and regulatory concerns. Ongoing research and development aim to address these issues and expand the technology’s potential applications.
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions and stores them in a secure and transparent manner. Each block in the blockchain contains a timestamp, a unique identifier, and a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together using cryptography, creating an unalterable and tamper-proof chain of data.
When a new transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to a network of nodes (computers) that collectively validate and approve the transaction. Once validated, the transaction is added to a new block and added to the chain of existing blocks. This process is referred to as mining, and the nodes that participate in it are called miners.
Miners compete to solve a complex mathematical puzzle, with the first one to solve the puzzle receiving a reward in the form of cryptocurrency. This process ensures that the blockchain remains secure and trustworthy, as any attempt to alter or delete a transaction would require a majority of the network’s computing power.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralization. There is no central authority or governing body that controls the blockchain, which means that it is not subject to the whims of any single entity. Instead, the network of nodes operates on a consensus mechanism, whereby decisions are made based on the agreement of a majority of participants.
Another important feature of blockchain technology is its immutability. Once a transaction has been added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This means that the blockchain provides an irrefutable record of all transactions that have occurred, making it a valuable tool for auditing and compliance.
In addition to its use in cryptocurrency transactions, blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications. It can be used to track the provenance of goods, verify the authenticity of documents, and enable secure voting systems. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that we will see even more innovative and exciting applications emerge.
Main Purpose Of Blockchain
Blockchain technology was originally developed to support digital currencies such as Bitcoin. However, over time, its potential applications have expanded to cover a wide range of industries and use cases. At its core, the main purpose of blockchain is to provide a secure and transparent way to store and transfer information.
One of the key features of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional databases, which are usually controlled by a central authority, blockchain networks are distributed across a network of computers or nodes. This means that there is no single point of failure or control, and the network is resistant to censorship or manipulation.
Another important feature of blockchain technology is its immutability. Once a transaction or piece of information has been added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This provides a high level of security and integrity to the data stored on the blockchain, as it is virtually impossible for anyone to tamper with the records.
The transparency of the blockchain is also a key aspect of its purpose. Every transaction or piece of information added to the blockchain is publicly visible, and can be viewed by anyone with access to the network. This means that there is a high degree of accountability and transparency in blockchain-based systems, as all parties can see the same information and can verify that it is accurate.
The main purpose of blockchain can be seen in its many potential use cases across a wide range of industries. For example, in finance, blockchain can be used to facilitate secure and transparent transactions, as well as to improve the efficiency of payment processing and other financial services. In healthcare, blockchain can be used to securely store and share patient records, while in supply chain management, blockchain can be used to track products and ensure their authenticity.
The main purpose of blockchain is to provide a secure and transparent way to store and transfer information, with the potential to revolutionize many industries and use cases. By leveraging its decentralized nature, immutability, and transparency, blockchain technology has the potential to transform the way we store and share data, and to enable new forms of trust and collaboration across a wide range of fields.
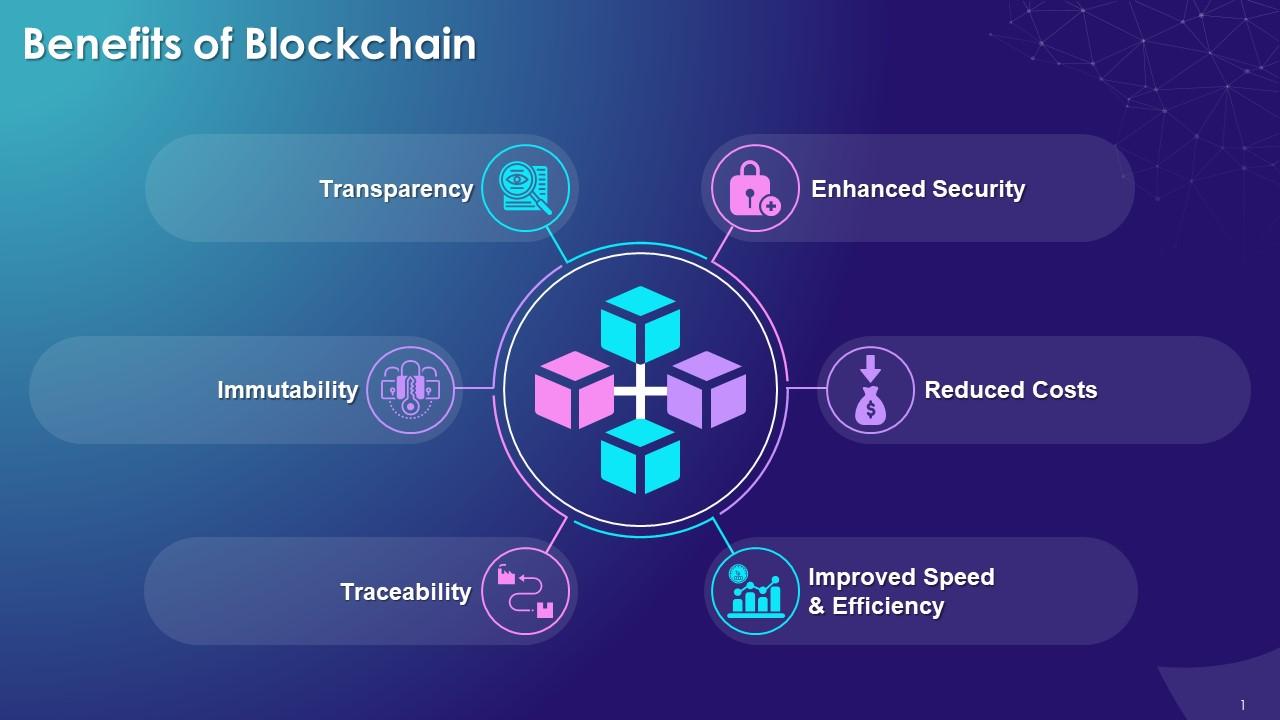
Advantages of blockchain technology
Decentralization:
One of the key advantages of blockchain technology is its decentralization. Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single authority controls everything, blockchain operates on a distributed network of computers. This means that there is no single point of failure, making it much more secure and resistant to hacking and cyber attacks.
Transparency:
Blockchain technology offers transparency in transactions. All transactions on the blockchain are recorded in a tamper-proof and transparent manner, which means that anyone can verify the authenticity of a transaction at any time. This feature helps in reducing fraud and corruption.
Efficiency:
Blockchain technology is highly efficient because it eliminates the need for intermediaries. Transactions can be processed much faster because there is no need for a middleman to validate and confirm them. This can save time and money, especially for businesses that deal with a high volume of transactions.
Security:
Blockchain technology offers high-level security because each transaction is recorded in a block and linked together in a chain. This makes it almost impossible for someone to alter or delete a transaction, making it more secure than traditional systems.
Cost savings:
Blockchain technology can significantly reduce costs because it eliminates the need for intermediaries and other third-party service providers. This can save businesses a lot of money, especially in industries like banking and finance, where there are many intermediaries involved in the process.
Immutable records:
Blockchain technology ensures that all records on the blockchain are immutable, meaning they cannot be altered or deleted. This makes it easier to track and verify transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing transparency.
Accessibility:
Blockchain technology is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, making it easy for anyone to participate in transactions on the blockchain. This feature can help to promote financial inclusion, especially in countries where traditional banking systems are not easily accessible.
Traceability:
Blockchain technology offers traceability, which means that it is easy to track the movement of assets or goods. This feature can be useful in industries like supply chain management, where it is important to track the movement of goods from the point of origin to the point of delivery.
Improved data management:
Blockchain technology offers improved data management because it allows for the creation of secure and tamper-proof databases. This can be useful in industries like healthcare, where data security and privacy are critical.
Trust:
Blockchain technology can help to build trust between parties because it offers a transparent and secure way to conduct transactions. This can be especially useful in industries like real estate, where trust between parties is critical.
Risks of blockchain
Blockchain technology has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. However, like any technology, blockchain also comes with its fair share of risks and challenges. In this response, we will explore some of the major risks associated with blockchain technology.
Security Risks:
Blockchain technology is touted as a secure method of storing data because of its distributed nature. However, it is not completely immune to security risks. One of the most significant security risks associated with blockchain is the potential for 51% attacks. In a 51% attack, an attacker gains control of more than half of the network’s computing power, allowing them to manipulate the blockchain’s transactions and potentially even steal funds. Other security risks include hacking attacks on individual wallets or exchanges, as well as vulnerabilities in smart contracts.
Regulatory Risks:
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology makes it challenging to regulate. This lack of regulation can lead to regulatory risks, such as a lack of legal clarity and uncertainty around the technology’s use in specific applications. Furthermore, governments may view blockchain technology as a threat to their control over financial systems and may seek to regulate or ban its use in some jurisdictions.
Scalability Risks:
While blockchain technology is highly secure and transparent, it can be challenging to scale. As the number of users and transactions on a blockchain network increases, it can become slower and more expensive to use. This scalability issue can be addressed through various methods, such as sharding, but it remains a significant challenge for many blockchain networks.
Interoperability Risks:
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, and there are numerous competing blockchain platforms and protocols. This can lead to interoperability risks, where it is challenging to integrate different blockchain networks and protocols. This lack of interoperability can limit the potential benefits of blockchain technology by making it difficult to share data and assets across different networks.
Environmental Risks:
Some blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin, rely on a process called mining to validate transactions and create new blocks. Mining requires significant amounts of energy, leading to concerns around the environmental impact of blockchain technology. While efforts are underway to develop more environmentally friendly consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake, these are still in the early stages of development.
Legal Risks:
The use of blockchain technology in various applications, such as smart contracts, raises legal risks. Smart contracts, for example, can be programmed to execute automatically based on predetermined conditions, leading to potential legal disputes if the contract’s terms are not met. Furthermore, the use of blockchain technology in certain industries, such as healthcare and finance, may raise additional legal and regulatory risks.
Conclusion
Overall, blockchain technology is a rapidly evolving field with enormous potential, and its impact on society and the economy is likely to continue to grow in the coming years. As the technology matures and new use cases emerge, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of blockchain solutions in various industries.
While blockchain technology has many benefits, it also has some limitations and challenges. One of the major challenges is scalability, as the current blockchain infrastructure can only process a limited number of transactions per second. Another challenge is the high energy consumption associated with some blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are three main types of blockchain: public, private, and consortium. Public blockchains are open to anyone, while private blockchains are only accessible to a specific group of people or organizations. Consortium blockchains are a hybrid of both public and private blockchains.
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that are encoded on the blockchain. They automatically enforce the terms and conditions of the contract without the need for intermediaries or third-party authorities.
A cryptocurrency is a digital asset that is designed to work as a medium of exchange. It uses blockchain technology to secure and verify transactions and to control the creation of new units.
A blockchain fork occurs when the blockchain network splits into two separate chains due to a disagreement in the rules of the network. This can result in the creation of a new cryptocurrency, such as the case of Bitcoin Cash and Ethereum Classic.
Mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain ledger. This process involves solving complex mathematical algorithms to create new blocks and earn rewards in the form of cryptocurrency.
Some of the limitations of blockchain technology include scalability issues, energy consumption, and lack of standardization. Additionally, since transactions on the blockchain are immutable, it can be difficult to correct errors or fraudulent activity.
Blockchain technology is being used in a variety of industries, including finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and voting systems. It is being used to create more efficient and transparent systems, reduce fraud and corruption, and improve security and privacy.